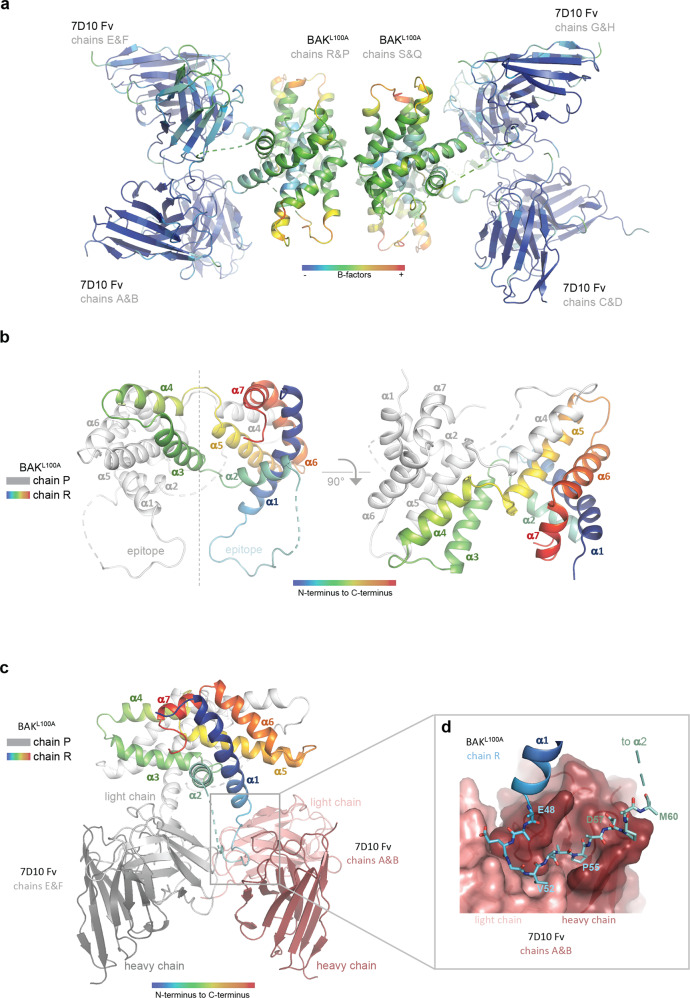
Fig. 2. Structure of the complex between antibody 7D10 and BAKL100A.
a The BAKL100A moieties of the complex have elevated B-factors. The crystallographic asymmetric unit contains four BAK polypeptides (central) with four attached Fv fragments. Colouring is by B factor (low-blue, high-red) indicating that the BAK parts of the image are more disordered. b In the crystal, BAKL100A is an α3α4 domain-swapped dimer. Chain R of the BAK dimer is coloured rainbow (blue - α1 through red - α7), and chain P in white. In the left panel the pseudo dyad symmetry axis is vertical. The cross-over connections between α4 and α5 are at the top of the figure. The cross-over connections between α2 and α3 are in the centre of the figure where the symmetry breaks down. This connection is built for the chain R (cyan - α2 to green - α3), but no interpretable electron density is observed for α3 on the chain P (white dashed lines). The epitope segments are at the bottom of the figure, the dashed lines indicating disorder in those parts of the α1-α2 loop C-terminal to the epitope. In the right panel the view is down the pseudo dyad symmetry axis. The cross-over connections between α4 and α5 are in the foreground near the symmetry axis. c The α3α4 domain-swapped BAKL100A dimer binds two copies of the 7D10 Fv fragment. The BAKL100A moieties occlude each other in this view. Chain R of the BAK dimer (coloured rainbow) engages Light chain Variable domain (light pink) and Heavy chain Variable domain (dark pink) in the foreground, with chain R (white) to Light chain Variable domain (light grey) and Heavy chain Variable domain (dark grey) at the rear. The crystal asymmetric unit contains two essentially identical copies of this dimer. d The BAK epitope snakes its way across a binding crevice in the 7D10 Fv (pink surface). BAK residues shown as sticks are 48EAEGVAAPADPEM60 with contacting residues in bold in the sequence. Side chains of E48, E59 and M60 are disordered and shown as alanine.