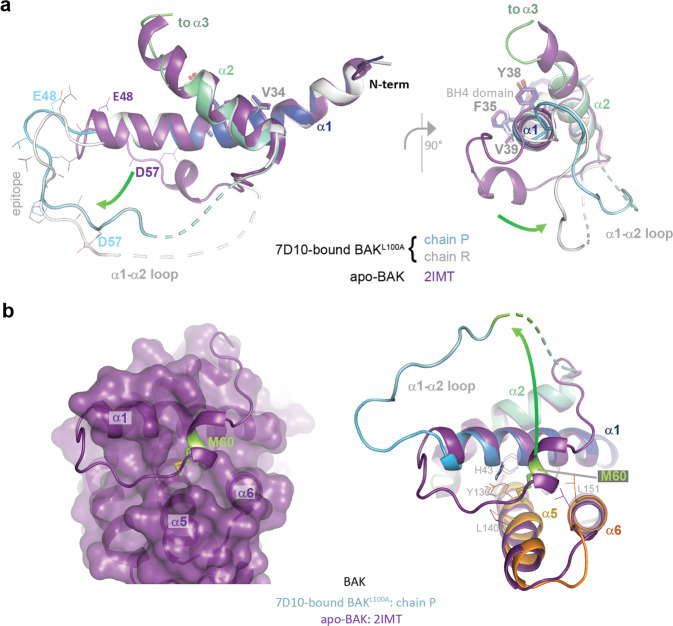
Fig. 3. Differences between apo- and 7D10-bound structures of BAK.
a Orthogonal views of the overlay of apo-BAK (2IMT - purple) on chains R (blue to cyan) and P (white) of the antibody-bound-BAKL100A, showing only helices α1 and α2. The views focus on the C-terminus of helix α1 and the movement of the α1-α2 loop comparing the structures (green arrow). The epitopes are lower right, involving amino acids from the single helical turn in the α1-α2 loop of the apo-BAK structure. Epitope residues are shown as lines, BH4 residues as sticks 34VFRSYV39. The antibody does not disturb the structure of α1, only of the α1-α2 loop. The C-terminus of α2 is where chain P becomes disordered and where chain R begins to be re-organised for the crossover connection to α3. Two different conformations are observed in the residues connecting the end of α1 to the epitope, 47QEAE50 indicative of the extraction of the loop from the helical fold by the 7D10 Fv engaging the epitope residues 51–57. b M60 is extracted from its conserved binding site in apo-BAK in the crystal structure of the complex with 7D10. The left panel shows a surface representation of the helical bundle of apo-BAK (2IMT - purple) illustrating how the α1-α2 loop (cartoon representation) engages at the surface of the protein, in particular via residue M60 (green) in the single helical turn. The right panel displays an overlay of helices 1, 5 and 6 of apo-BAK (2IMT - purple) and chain P of antibody-bound-BAK (blue to orange), showing M60 (green) in a pocket defined by helices 1, 5 and 6 in apo-BAK and dislodged from that pocket in the 7D10 complex (arrow). The receptor site for M60 is not significantly disturbed by M60’s removal in the 7D10 complex (residues shown as sticks). M60 is not ordered in any of the four BAK polypeptides in the crystal structure of the complex.