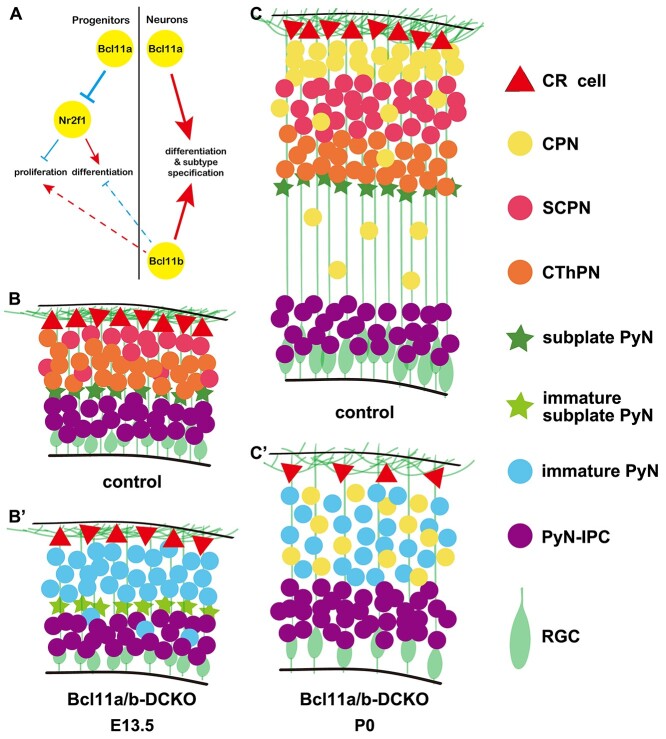
Figure 11.
Summary of Bcl11a and Bcl11b functions in cortical projection neuronal development. (A) An integrated diagram illustrating the genetic interactions of Bcl11a and Bcl11b play essential roles in different types of neurons. The red arrows indicate the positive regulation, while the blue arrows indicate the negative regulation. The dashed lines mean possible feedback regulations. (B–C′) Conditional deletion of both Bcl11a and Bcl11b results in depletion and premature differentiation of cortical RGCs, and blockage of cortical projection neuron differentiation at E13.5 and P0. This study showed that the proper intrinsic clock of proliferation and differentiation at early neurogenesis was disrupted in the absence of Bcl11a and Bcl11b, followed by precocious RGCs lineage switch. The projection neurons of the Bcl11a/b-DCKO mice failed to acquire distinct subtype identities at P0. CR cell, Cajal–Retzius cells; CPN, callosal projection neurons; SCPN, subcerebral neurons; CThPN, corticothalamic neurons; PyN, projection neurons; PyN-IPC, projection neuron intermediate progenitors; RGC, radial glial cells.