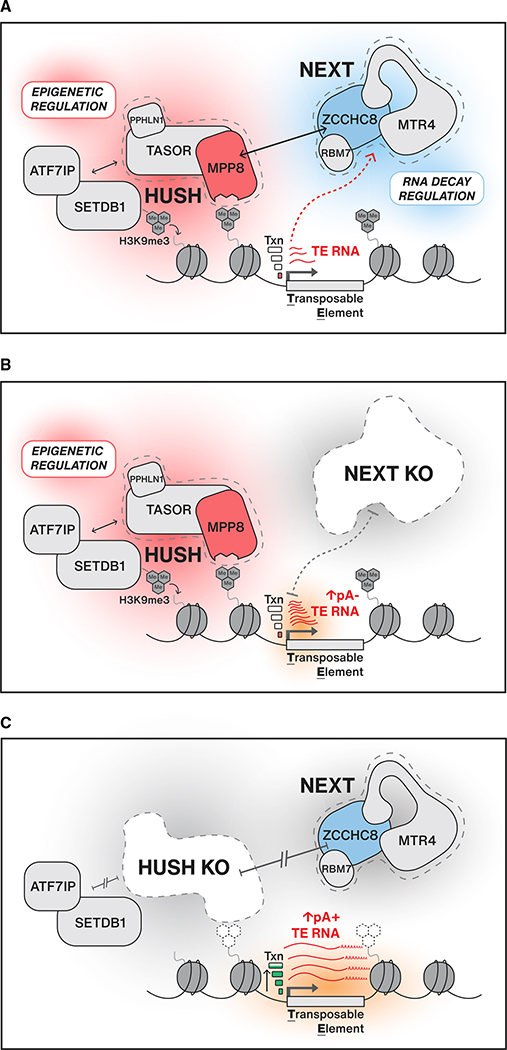
Figure 6. Model.
(A) The HUSH and NEXT complexes function to control expression of TE transcripts at either the transcriptional or post-transcriptional level, respectively. HUSH is recruited to TE loci decorated with H3K9me3 histone marks and is required for maintaining H3K9me3 levels and transcriptional (txn) suppression. NEXT is recruited to HUSH-bound loci through a physical connection that requires ZCCHC8 and MPP8.
(B) In the absence of NEXT, HUSH can still bind to chromatin, regulate H3K9me3, and maintain low transcription levels. Without NEXT-mediated RNA decay, short pA− transcripts from TE loci are stabilized.
(C) In the absence of HUSH, H3K9me3 levels are not maintained and NEXT is no longer recruited to HUSH-bound loci. TE loci lose transcriptional repression and show an increase in full-length pA+ TE RNAs that, in the case of L1 LINEs, can be export competent and subsequently translated.