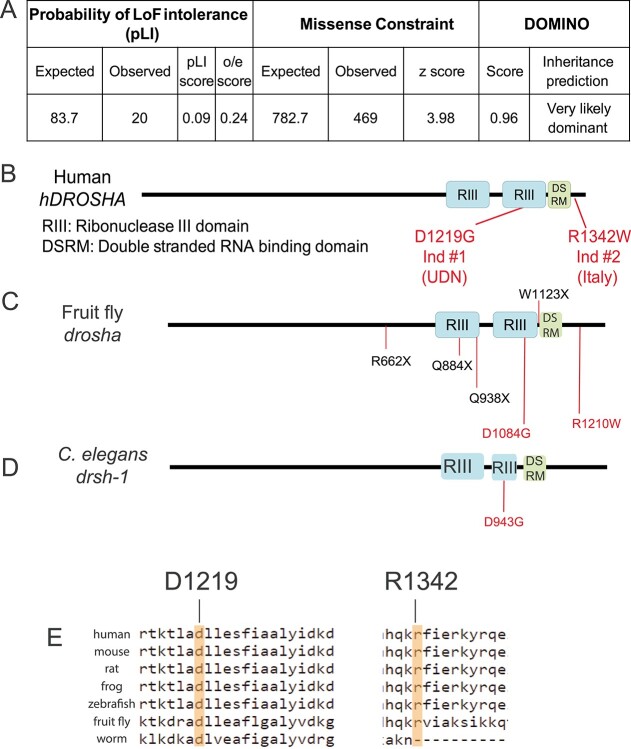
Figure 2.
DROSHA is variant constrained and its protein structure is highly conserved. (A) Bioinformatics analysis of DROSHA genetic variants from the gnomAD (59). DROSHA has an observed/expected (o/e) score of 0.24, which suggests that is not tolerant to loss-of-function variants. It also has a high missense constraint score of 3.98 and is predicted to be very likely dominant by DOMINO (106). (B–D) Protein structure of human (B), fruit fly (C) and C. elegans (D). DROSHA proteins are highly conserved in the three species, with all proteins containing two Ribonuclease III domains (RIII) and a single DSRM domain. The residues affected by the patient variants are shown in red in (B) and their corresponding residues are shown in (C–E). Drosha truncation mutations that have been annotated as null alleles are labeled in black in (C). (E) Conservation of affected patient residues. Both Individual 1 (left) and 2’s (right) variants affect residues that are conserved between humans and flies but only Individual 1’s residue is conserved in all three species.