Figure 4.
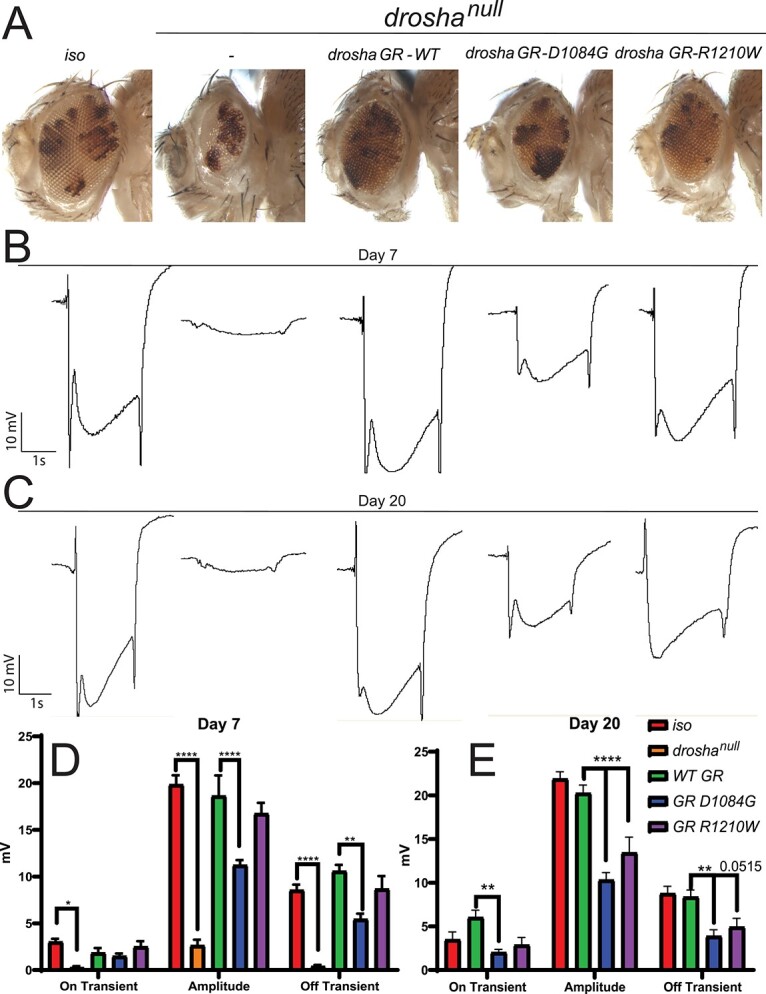
DROSHA variants can cause progressive neural defects in the fly eye (A) drosha eye-specific mutant clones generated by the eyeless (ey)–Flippase (FLP) system cause a significant reduction in the size of the eye and head and GR constructs produce similar rescue effects to Figure 3B–E. (B, C) Representative ERG traces from control (iso) and drosha mutant and GR flies at day 7 (B) and day 20 (C). Quantification in (D) and (E). Drosha null mutants show effectively no response to light, whereas wild-type GR flies fully respond compared to iso flies (B–E). Droshanull responses were not quantified at day 20 because no progressive effect could be seen due to the lack of response at day 7. Only D1084G flies show ERG defects at day 7 (B, D) but both D1084G and R1210W flies show statistically significant defects at day 20 particularly in amplitude (C, E) suggesting that the R1210W variants lead to a progressive neural defect. Off transient defects in R1210W flies approach significance (P = 0.0515). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001, ***P < 0.0001.
