Figure 1.
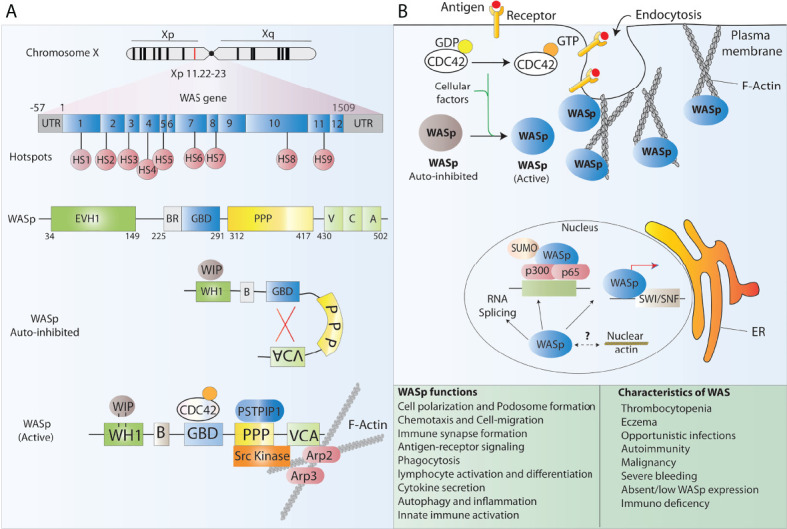
WASp structure and function. (A) Schematic representation of the WAS gene and its major functional protein domains. The WAS gene is located on the X chromosome and comprises 12 exons. Disease-causing mutations in WAS patients are scattered around the whole gene, however, 9 mutational hotspots (HS) have been detected in patients. WASp is made of 5 different domains and presents in the cell cytoplasm in an auto-inhibited conformation at resting state and leads to actin polymerization after receptor stimulation. (B) The many functions of WASp in lymphoid and myeloid immune cells relate to its role in regulating the polymerization of new branched actin filaments. Besides, WASp plays an important role as a scaffold protein in the regulation of some nuclear functions such as chromatin remodeling.
