Figure 2.
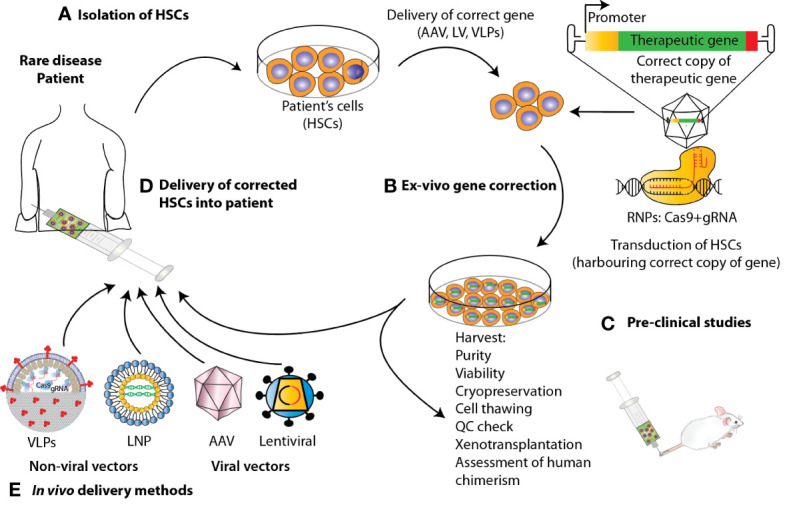
State-of-the-art ex vivo and in vivo gene therapy and gene editing strategies applied to HSPCs to correct blood genetic disorders via delivery of a corrective gene. Schematic representation of the various steps involved in the development of a therapeutic product for the treatment of blood diseases via gene therapy. For the ex-vivo approach, (A) HSPCs are isolated from mobilized peripheral blood (mPB) apheresis. (B) Using CRISPR/Cas9-based gene editing or LV carrying the gene of interest, these cells are edited/transduced ex vivo and (C) after performing a thorough safety and efficacy quality control (QC) on the product (D) cells are infused back to the patient after pharmacokinetically adjusted myeloablation. (E) When performing gene therapy in vivo, the correct copy of the gene is directly infused into the patient via the use of viral vectors or non-viral methods such as Virus-like Particles (VLPs) and lipid nanoparticles (LNPs).
