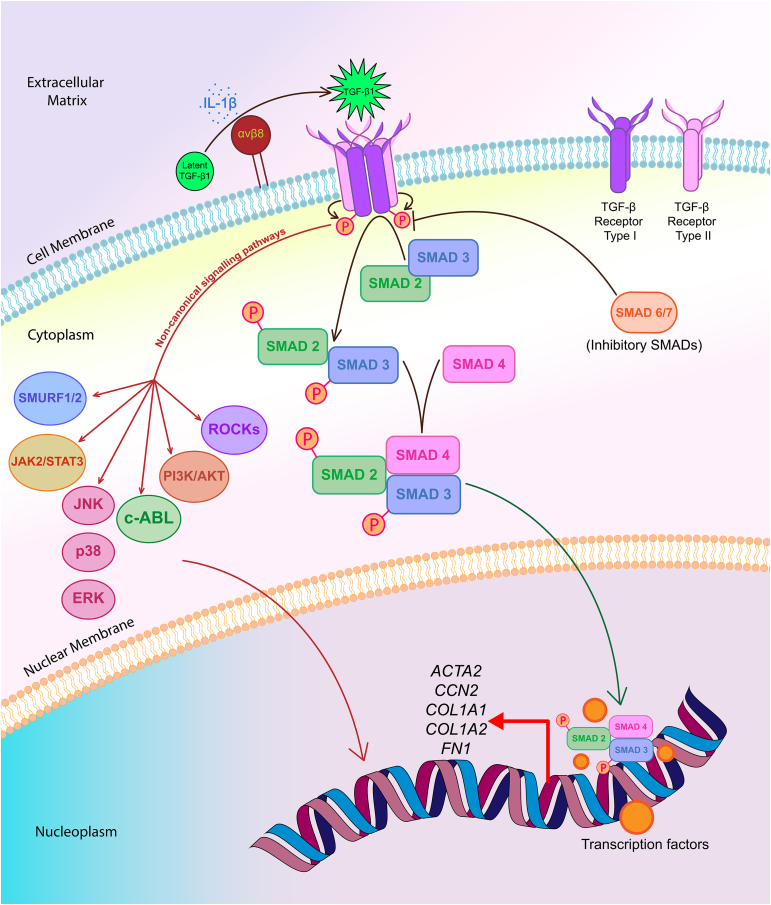
Figure 1.
A simple illustration of TGF-β signalling pathways in lung (myo)fibroblasts leading to the increased expression of profibrotic genes in these cell types. In the extracellular matrix (top), IL-1β, a proinflammatory cytokine triggers the integrin αvβ8-mediated conversion of latent TGF-β1 protein to its active form. On the cell membrane, activated form of TGF-β1 homodimers (green star) bind to transmembrane and dimeric TGF-β receptor type II (TβRII) and leads to the recruitment of dimeric TGF-β receptor type I (TβRI) inducing the formation of a heterotetrameric receptor complex. Subsequently, this ligand binding triggers the phosphorylation and activation of TβRI by TβRII (small curved brown arrows). On the cytoplasmic side, the activated TβRI then binds and phosphorylates SMAD2 and SMAD3, also known as receptor regulated SMADs (R-SMADs), to drive the TGF-β canonical signalling pathway. These two SMADs get transported into the nucleus as a complex with SMAD4 (curved green arrow), where they interact with other transcription factors to upregulate the expression of various profibrotic genes, including ACTA2, CCN2, COL1A1, COL1A2 and FN1 in the fibroblasts and myofibroblasts of lung. The inhibitory SMADs, namely SMAD6/7, bind with TβRI to prevent recruitment and phosphorylation of the R-SMADs, which dampen TGF-β signalling thereby blocking the transcription of genes encoding profibrotic factors. In addition, the activated TGF-β1 ligand bound to its receptors can signal through various non-canonical pathways, including ones involving MAPKs (ERK, JNK, p38), PI3K/AKT, c-ABL, JAK2/STAT3, SMURF1/2 and ROCKs. Some of these mediatory signalling cascades can act either directly (single curved red arrow), or in association with SMAD proteins, to regulate gene expression and have pathophysiological roles in fibrotic disorders, such as IPF.
The abbreviation of SMAD/Smad is expanded as follows: Acronym from the fusion of Caenorhabditis elegans SMA ("small" worm phenotype) and MAD ("Mothers against Decapentaplegic") proteins in Drosophila melanogaster.
Expanded names of members of the non-canonical TGF-β pathways: AKT/Akt, Ak (mouse strain) transforming. Originally identified as an oncogene in the transforming retrovirus. It is also known as Protein kinase B; c-ABL, A tyrosine kinase encoded by Abelson murine leukaemia viral oncogene homologue 1 in human beings; ERK, Extracellular receptor kinase; JAK2, Janus kinase 2; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; MAPK(s), Mitogen-activated protein kinase(s); p38, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; PI3K, Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; ROCKs, Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinases; SMURF1/2, SMAD ubiquitination regulatory factor 1/2; STAT3, Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.
Names of proteins encoded by the profibrotic genes: ACTA2, encodes Actin alpha 2, smooth muscle in humans; CCN2, encodes Cellular communication network factor 2; COL1A1, encodes Collagen type 1 alpha 1 chain; COL1A2, encodes Collagen type 1 alpha 2 chain; FN1, encodes Fibronectin 1.