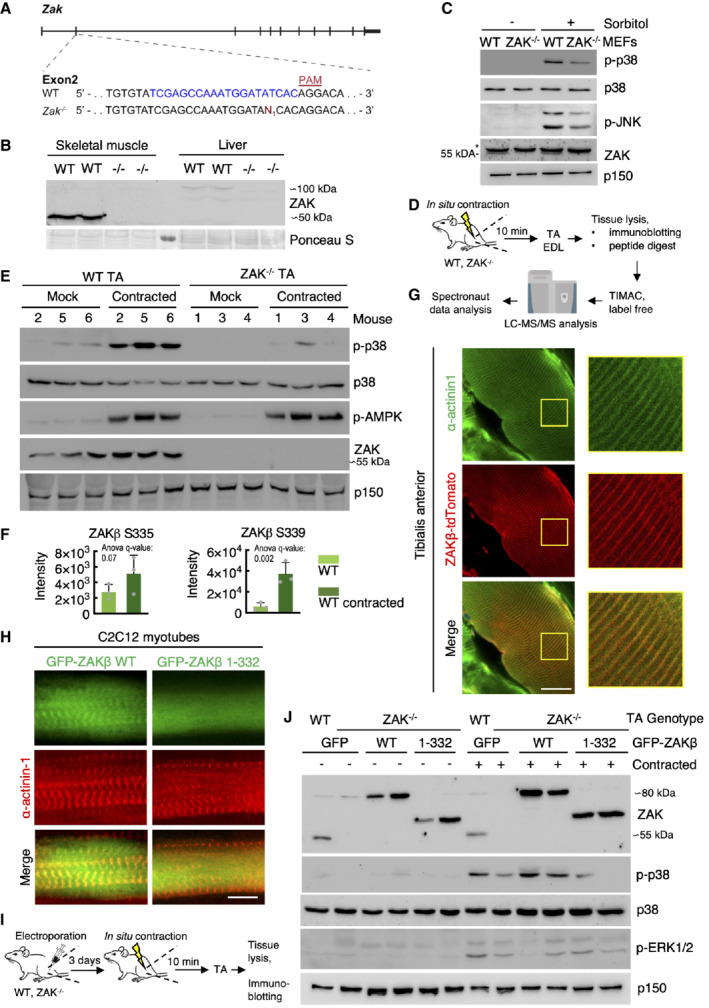
Figure 4. Z‐disc localized ZAKβ is activated by muscle contraction.
-
AGenomic location of guide‐RNA sequence (blue) and a derived knockout allele in exon 2 of the murine ZAK gene. PAM—protospacer adjacent motif.
-
BSkeletal muscle (tibialis anterior, TA) and liver from WT and ZAK−/− mice were lysed and analyzed for ZAK isoform expression by immunoblotting. Ponceau staining of the membrane indicates equal loading.
-
CMouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEF) isolated from WT and ZAK−/− mice were treated with 500 mM sorbitol (1 h). Lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. *—unspecific band.
-
DSchematic of in situ muscle contraction experiments. Mice were anesthetized, and one of the lower hindlimbs was subjected to electrically stimulated contraction (10 min.). Upon euthanization, tibialis anterior (TA) and extensor digitorum longus (EDL) muscles were isolated. Tissue homogenates were processed for immunoblotting (e) or proteins were subjected to trypsin digestion, phospho‐peptide enrichment, and label‐free quantification by mass spectrometry.
-
E16‐18‐week‐old WT and ZAK−/− male mice (n = 3 biological replicates) were subjected to the protocol in (D). TA lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies.
-
FZAKβ S335 and S339 phosphorylation sites upregulated in WT TA muscles from (D). Values indicate absolute phospho‐peptide abundances and error bars represent the standard deviation (n = 3 biological replicates).
-
GTA muscle in an 8‐week‐old WT male mouse was electroporated with a ZAKβ‐tdTomato construct. After 7 days the muscle was harvested, sectioned longitudinally, and immunostained with an antibody against the Z‐disc marker α‐actinin1. The right panel shows a higher magnification of the region highlighted in yellow.
-
HC2C12 cells were differentiated into myotubes for 14 days and transfected with the indicated GFP‐ZAKβ constructs. Cells were fixed and immunostained with an antibody against α‐actinin1.
-
ISchematic of electroporation rescue experiments. TA muscles were electroporated with GFP‐ZAKβ constructs. After 3 days the muscles were exposed to in situ contraction and processed for immunoblotting.
-
J16‐18‐week‐old WT and ZAK−/− male mice were subjected to the experimental protocol in (I). TA muscle lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies.
Data information: All scale bars, 20 μm.
Source data are available online for this figure.
