-
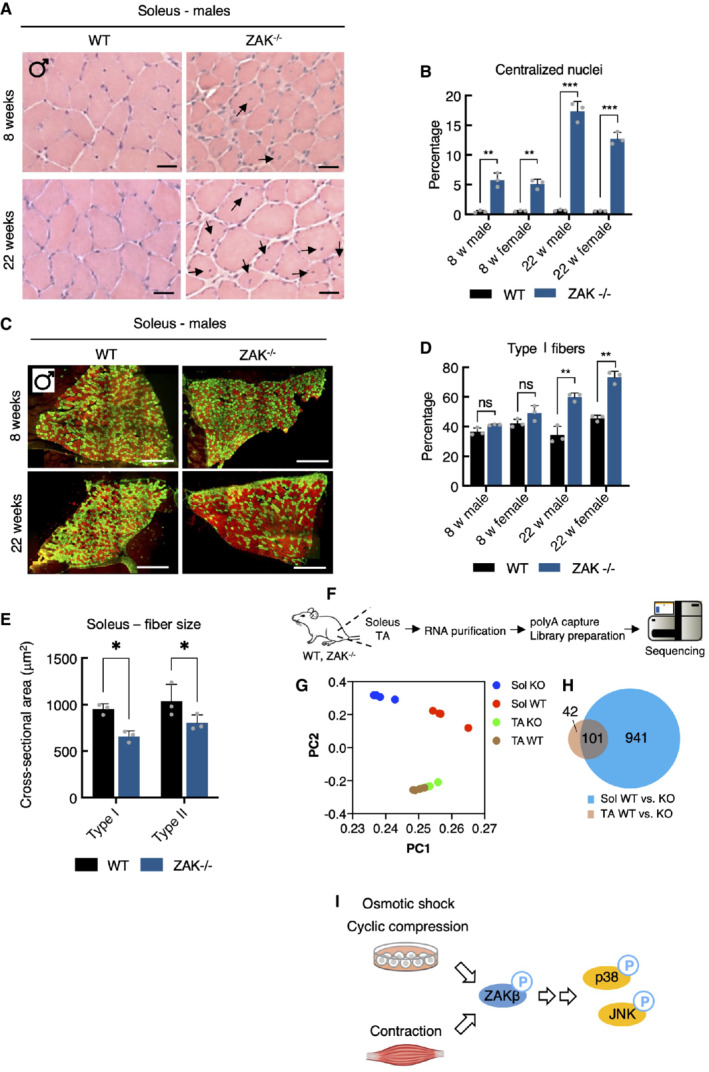
A
H&E staining of soleus muscle cross‐sections from 8‐ and 22‐week‐old WT and ZAK−/− male mice. Arrows indicate the presence of centralized nuclei. Scale bars, 50 μm.
-
B
Quantification of (A). Values indicate the percentage of fibers displaying centralized nuclei and error bars represent the standard deviation (n = 3 biological replicates). **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 in t‐test with the Bonferroni–Dunn correction for multiple comparison.
-
C
Muscles from (A) were immunostained for type I (red) and type IIa (green) fibers using myosin isoform‐specific antibodies. Scale bars, 500 μm.
-
D
Quantification of (C). Values indicate the percentage of fibers positive for type I myosin and error bars represent the standard deviation (n = 3 biological replicates). **P < 0.01 and ns, not significant in t‐test with the Bonferroni–Dunn correction for multiple comparison.
-
E
Cross‐sectional area of type I and type IIa fibers in soleus from 8‐week‐old WT and ZAK−/− male mice. Values indicate the mean from one specimen and error bars represent the standard deviation (n = 3 biological replicates). *P < 0.05 in 2‐way ANOVA corrected for multiple comparison using FDR (Benjamini, Krieger, and Yekutieli).
-
F
Schematic of muscle transcriptomic analysis. Soleus and TA muscles were isolated from 16‐18‐week‐old WT and ZAK−/− female mice (n = 4 biological replicates). Purified RNA was subjected to polyA capture and deep sequencing.
-
G
Principal component analysis of the data obtained from (F).
-
H
Venn diagram from (F) of the overlap of differentially expressed genes (DEG) in soleus (Sol, blue) and TA (brown).
-
I
Mechanical perturbation of cells by osmotic shock, compression, and muscle contraction activates ZAKβ and downstream kinases p38 and JNK. These reactions are dependent on sensing of stress fiber/Z‐disc deformation by the ZAKβ SFBD domain.