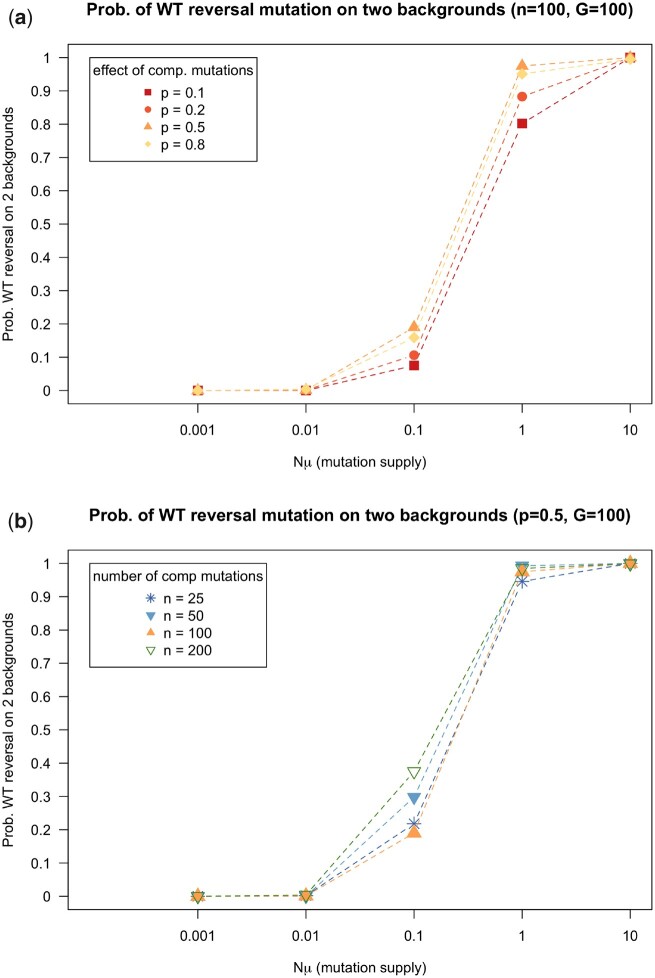
Fig. 3.
a) The probability that a reversal mutation to the WT phenotype occurs on 2 different backgrounds, i.e. from the resistant clone without a compensatory mutation (Res to WT), and a resistant clone carrying a compensatory mutation (Com to CR). In these simulations, resistant clones with compensatory mutations can acquire a second mutation (i.e. they can revert to the wild-type phenotype via compensated resistance, CR). Simulations are run for 100 generations and for each parameter combination we run 1,000 simulations. b) Similar to (a), but simulations are run for different values of n, the target size for compensatory mutations. Simulations are run for 100 generations. Other parameters: N = 10,000, c = 0.15, n = 100, P = 0.5. A mutation is considered to be present if at least present in 10 individuals (0.1% of the population).