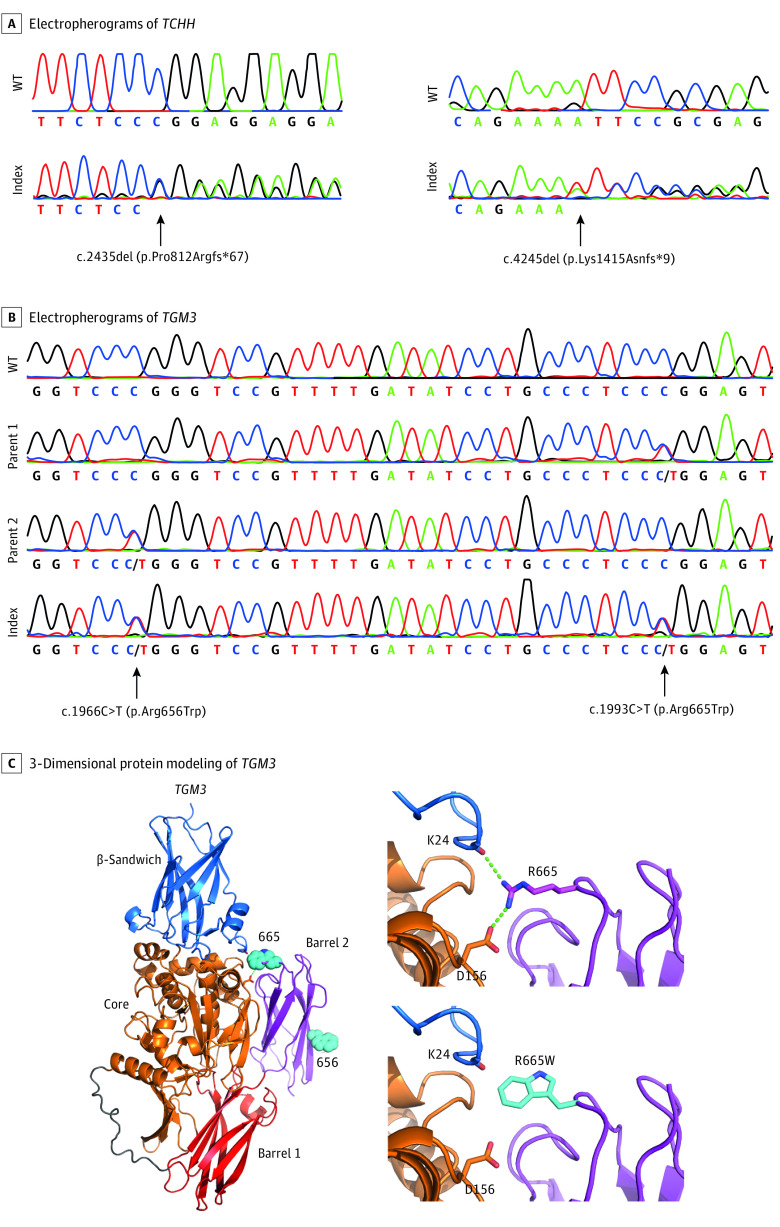
Figure 4. Newly Discovered Pathogenic Variants in TCHH and TGM3.
Electropherograms showing the newly discovered pathogenic frameshift variants c.2435del (p.Pro812Argfs*67) and c.4245del (p.Lys1415Asnfs*9) in TCHH (A) and the compound heterozygous pathogenic missense variants c.1966C>T (p.Arg656Trp) and c.1993C>T (p.Arg665Trp) in TGM3 (B) in comparison with the respective wild-type (WT) sequences. Protein modeling suggests that mutation p.Arg665Trp leads to the loss of 2 hydrogen bonds destabilizing the contact of barrel 2 domain to the core domain (C). Domain organization of TGM3 and location of residues 656 and 655 is indicated (C, left). Arg655 forms hydrogen bonds to the side chain of Asp156 and the backbone carbonyl of Lys24 (C, right upper panel). The mutation of Arg655 to Trp abolishes these hydrogen bonds (C, right lower panel).