Figure 5. Genetic Spectrum of UHS and Common Haplotypes Surrounding the Most Common PADI3 Pathogenic Variants.
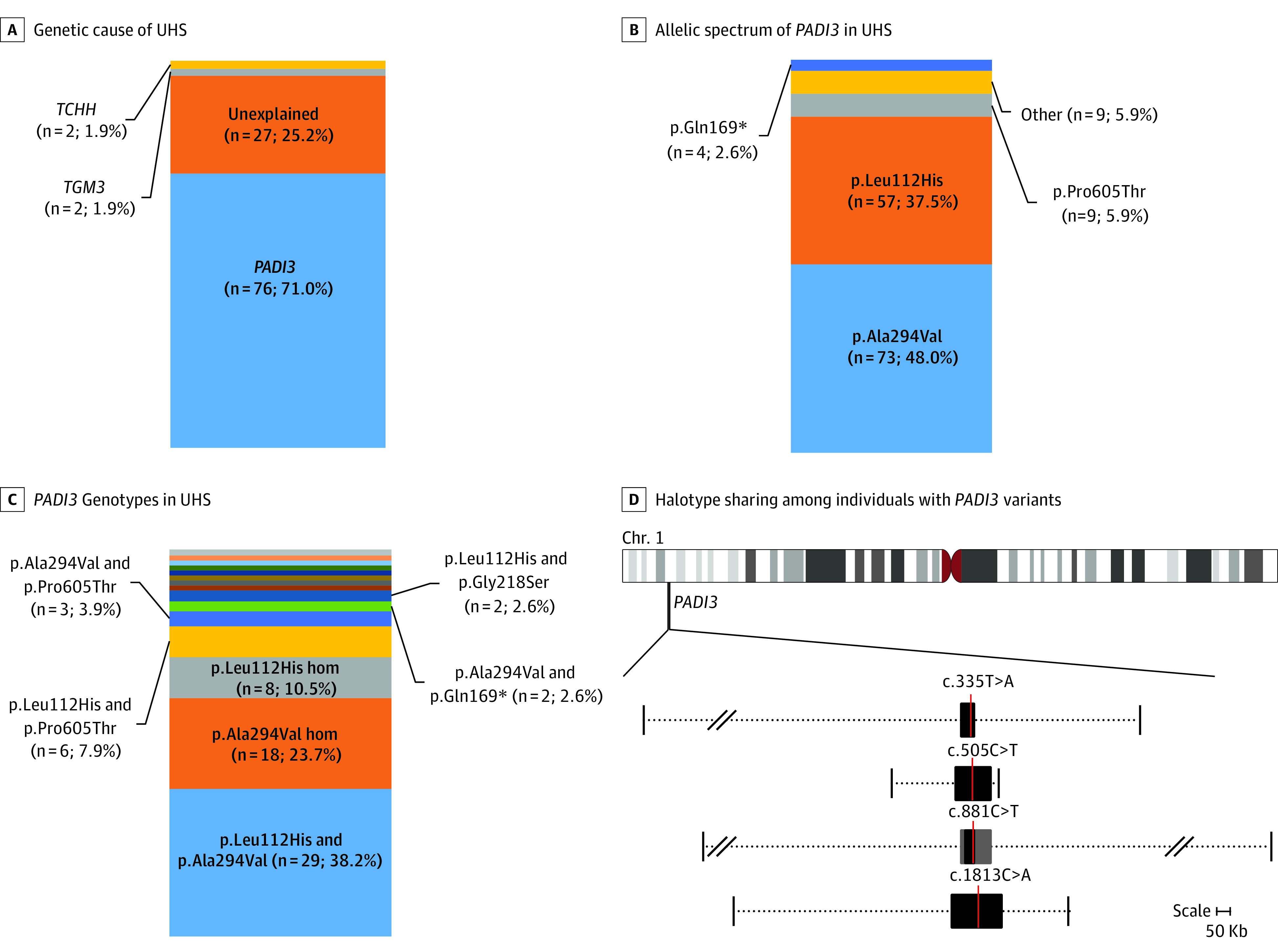
A, Stacked percentage bar plots depict the respective proportion of affected index cases that could be explained by pathogenic variants in either 1 of the 3 known uncombable hair syndrome (UHS)-associated genes and those not yet genetically elucidated within the total cohort. B, Individual pathogenic variants within all mutated PADI3 alleles (other includes p.Gly22Trp [n = 1], p.Arg186Trp [n = 1], p.Gly218Ser [n = 2], p.Arg372Gly [n = 1], p.Arg372Met [n = 1], p.Glu395Asnfs*7 [n = 1], p.Lys578* [n = 1], and p.Pro623Leu [n = 1]). C, Pathogenic genotypes within all PADI3-associated UHS cases: p.Gln169* homozygous; p.Leu112His and p.Glu395Asnfs*7; p.Leu112His and Arg186Trp; p.Leu112His and p.Arg372Met; p.Leu112His and p.Gly22Trp; p.Ala294Val and p.Arg372Gly; p.Ala294Val and p.Pro623Leu; and p.Ala294Val and p.Lys578* were singleton observations represented with different color codes without text, and each constitutes approximately 1% of the bar plot. D, The minimally shared regions across all haplotypes carrying a pathogenic variant are denoted with black boxes, and the location of the respective variations are depicted with a red line. The gray boxes surrounding c.881C>T denote a common haplotype shared over 90% of all analyzed haplotypes. The variable extent of haplotype sharing across all analyzed samples is denoted by the dotted lines, whereby the vertical lines on either end of the dotted lines mark the furthest extent of haplotype sharing between at least 2 samples upstream and downstream of the respective pathogenic variants. Slash marks show omitted whole sizes owing to space restraints. See eFigure 5 and eTables 2 through 5 in the Supplement for a depiction of haplotype sharing on individual level.
