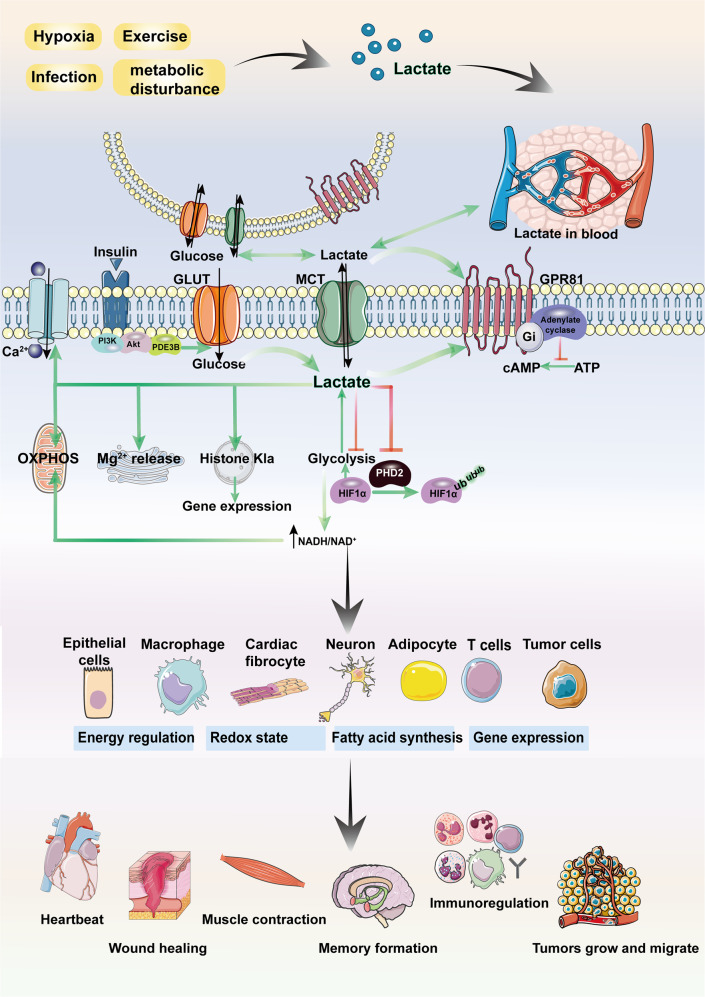
Fig. 2.
Lactate is involved in the regulation of cellular physiological and pathological processes. In addition to the intracellular production of lactate, lactate can enter target cells through intercellular shuttling involving nonchannel pathways or MCT1. As a signaling molecule or metabolic substrate, lactate is involved in glucose metabolism, fatty acid synthesis, redox homeostasis, and the PTM of proteins. Meanwhile, as a GPR81 ligand, lactate stimulates the GPR81 signaling pathway. Lactate has been shown to regulate muscle contraction, wound healing, memory formation, and tumor development. MCT monocarboxylate transporter; OXPHOS oxidative phosphorylation; GLUT glucose transporter. (Figure was partly created with SMART – Servier Medical ART)