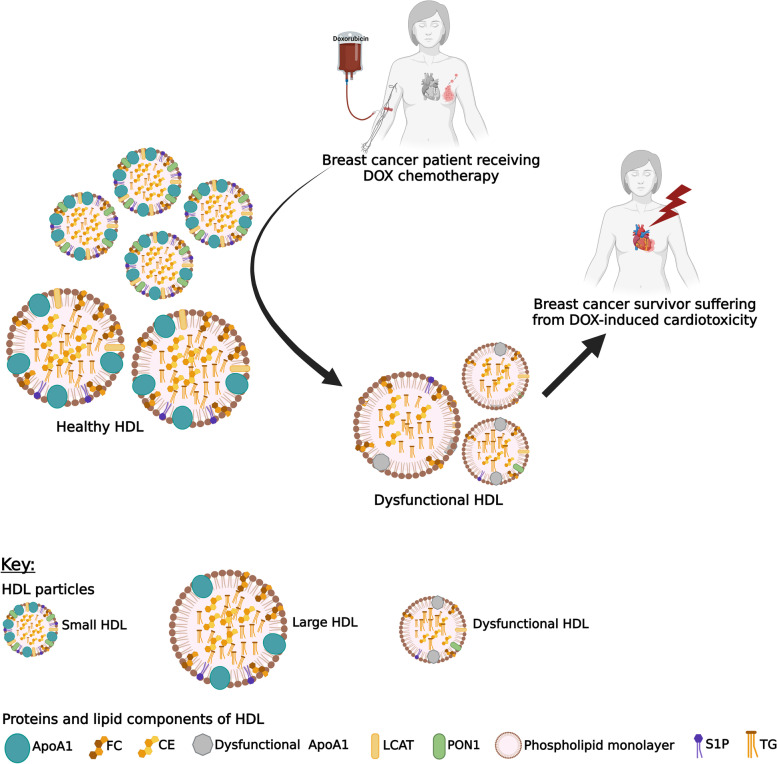
Fig. 1.
Proposed mechanism depicting the role of HDL in doxorubicin-induced cardiac toxicity. We propose that a shift in high-density lipoproteins (HDL) subclasses in breast cancer patients treated with doxorubicin leads to dysfunctional HDL with reduced anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, reverse cholesterol transport function and anti-apoptotic function that may facilitate the cardiac damage associated with the treatment of doxorubicin
Abbreviations: ApoA1 Apolipoprotein A1, CE Cholesteryl ester, DOX Doxorubicin, FC Free cholesterol, HDL High-density lipoprotein, LCAT Lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase, PON1 Paraoxonase 1, S1P Sphingosine-1-phosphate, TG Triglyceride