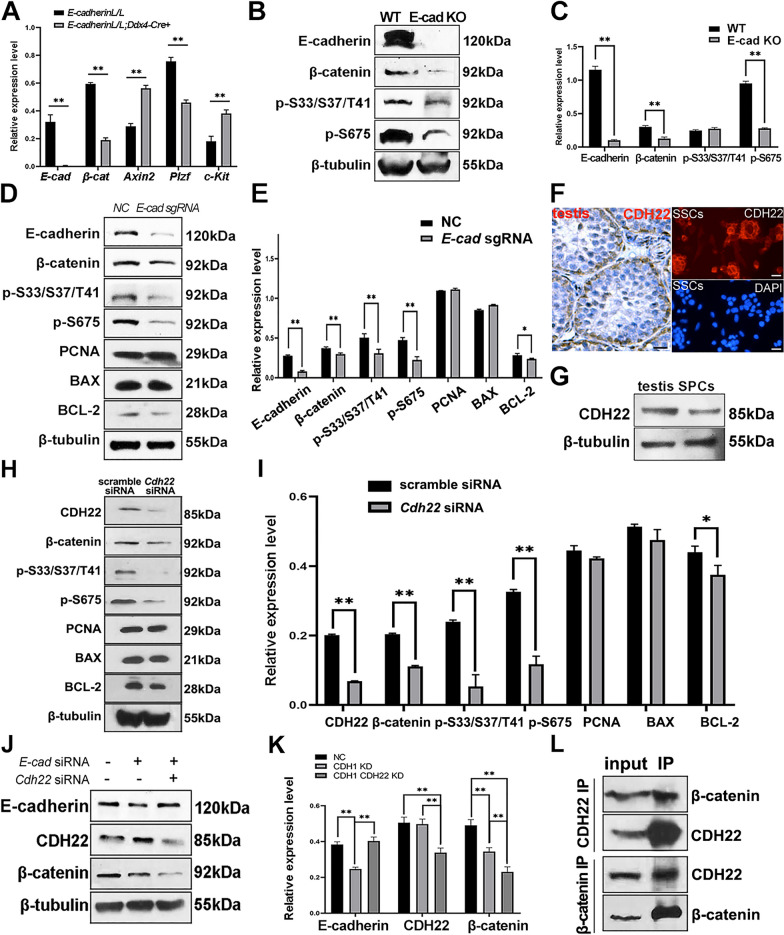
Fig. 3.
The expression of β-catenin was regulated by E-cadherin knockout in SPCs. Expression levels of E-cadherin, β-catenin, Axin2, Plzf and c-Kit mRNA were detected in SPCs from E-cadherinL/L and E-cadherinL/L;Ddx4-Cre+ mice using real time-qPCR (A). The expression levels of E-cadherin, β-catenin, and β-catenin phosphates (S33/S37/T41 and S675) were detected in SPCs from both genotypes (B) using Western blot, and were statistically analyzed (C). The expression levels of E-cadherin, β-catenin, and β-catenin phosphates (S33/S37/T41 and S675), PCNA, BAX, BCLL-2 and β-tubulin in E-cadherin deleted SPCs mediated CRISPR/Cas9 were detected using Western blot, n=3 (D), and were statistically analyzed (E). CDH22 was detected in 20-day mouse testes (left) and freshly isolated SPCs from 5-day mice (right, top: CDH22, down: DAPI) (F). A single band of CDH22 was detected in mouse testis and SPCs (G). Phosphorylation at S33/S37/T41 and S675 of β-catenin, and expression levels of CDH22, β-catenin, PCNA, BAX, BCL-2 and β-tubulin were detected in SPCs transfected with scramble or E-cadherin siRNA (H), and were statistically analyzed (I). Expression of E-cadherin, CDH22 and β-catenin in SPCs transfected with scramble, E-cadherin siRNA, or E-cadherin siRNA plus Cdh22 siRNA was evaluated with Western blot, n=3 (J), and were further statistically analyzed (K). The binding of CDH22 and β-catenin was verified with co-IP (L). Scale bar = 20 μm, data represent as mean ± SD, *p<0.05, **p<0.01