FIGURE 1.
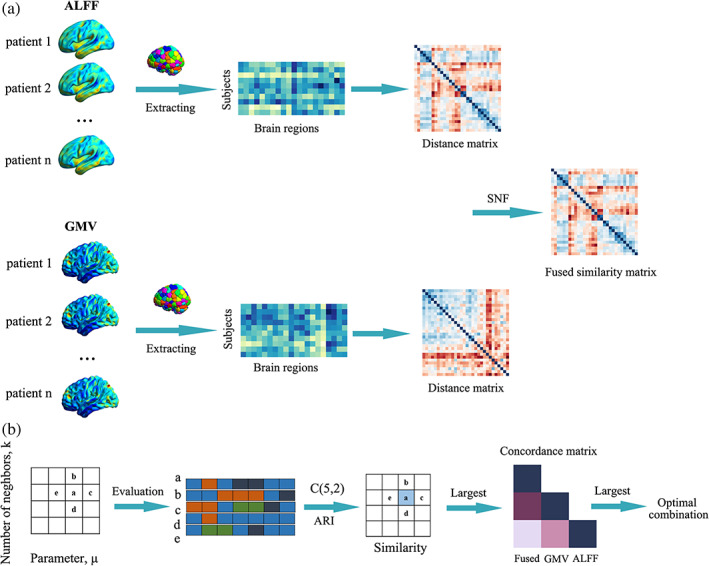
The workflow of subtyping strategy integrating multimodal information. (a) Multimodal (amplitude of low‐frequency fluctuation [ALFF] and gray matter volume [GMV]) distance networks were constructed and then integrated into one fused network using similarity network fusion (SNF). (b) Strategy to determine the optimal combination of K and μ. Here, we defined a similarity matrix to measure the consistency of subtyping results for each node in the hyperparameter space. For a given node “a” in hyperparameter space and its four neighbors (b, c, d, and e), we obtained their corresponding subtyping results. Adjusted rand index (ARI) was used to measure the similarity between subtyping results obtained from each pairs of five nodes (C(5,2) = 10). The local similarity of “a” was defined as the average ARI value of each pairs of subtyping results. A larger local similarity value meant a more stable subtyping result. The largest values in the similarity matrix were found out. Then we calculated consistency values between each pairs of structural, functional and the fused distance network for each node with the largest local similarity values (yielding a concordance matrix for each node). Among these, we picked the node where the average consistency value was the largest.
