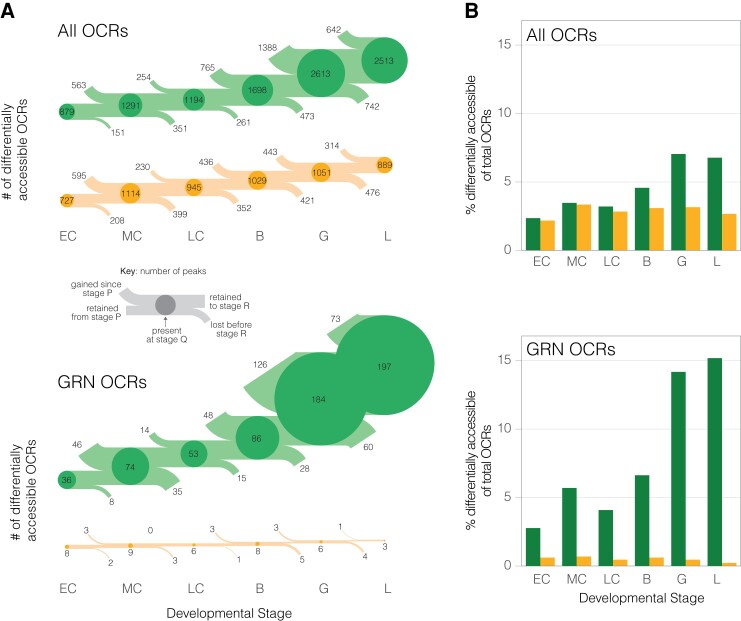
Fig. 3.
The chromatin landscape of the derived life history is far less accessible than that of species with the ancestral life history mode, particularly near core dGRN genes. (A) Number (flow diagram) and (B) percentage (barplots) of OCRs that are significantly differentially accessible in H. erythrogramma or species with the ancestral life history strategy for all orthologous OCRs (top) and only OCRs near dGRN genes (bottom). A key for flow diagrams is provided to explain how the number of differentially accessible OCRs are gained, retained, and lost between developmental stages. Circle size is proportional to the percentage of each set of OCRs (those near all genes or only dGRN genes) that are differentially accessible at a given stage for either H. erythrogramma or species with the ancestral developmental mode. OCR: open chromatin region; dGRN: developmental gene regulatory network.