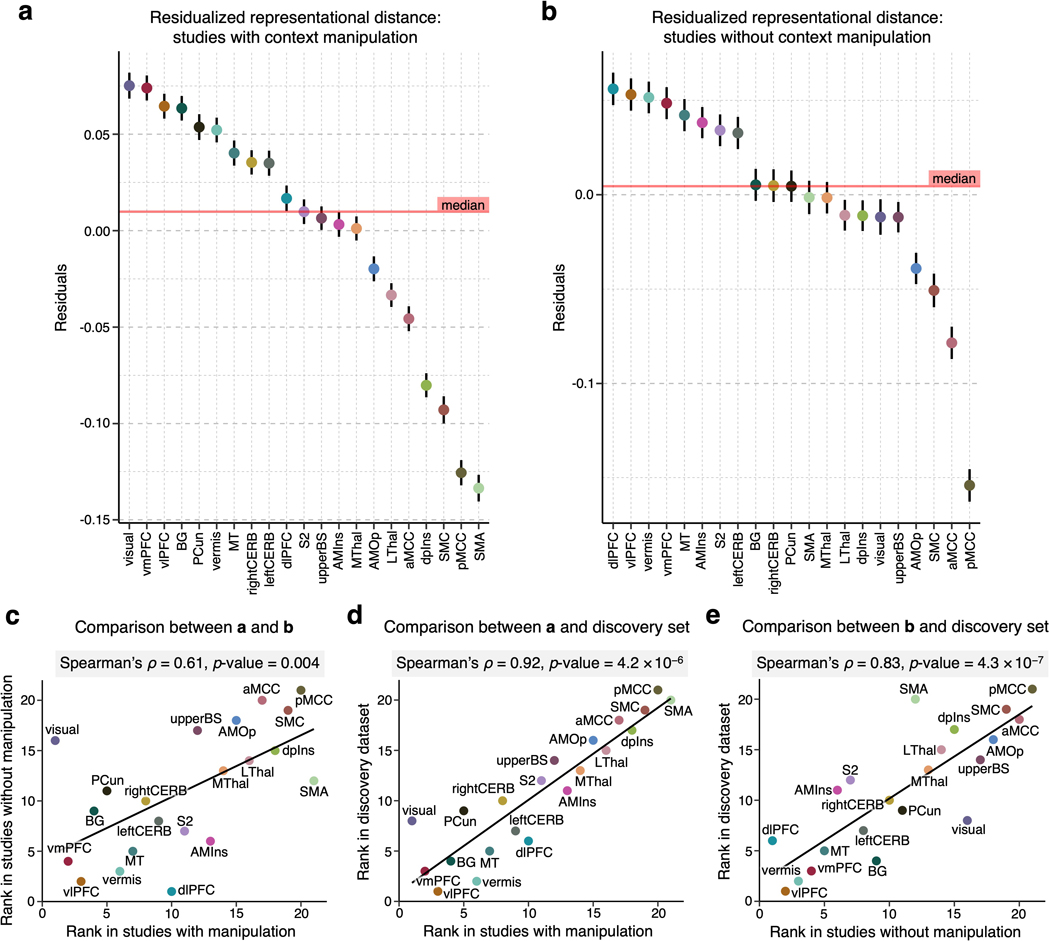
Extended Data Fig. 5. Results of the representational similarity analysis for studies with and without context manipulation.
We performed the representational similarity analysis and controlled for the region size in the discovery dataset divided into studies (a) with context manipulation (e.g., placebo and cognitive regulation; studies 1, 4, 6, 7, 8, 11, and 12; n = 229) and (b) without context manipulation (studies 2, 3, 5, 9, 10, and 13; n = 175). The figures show the mean residualized representational distance and the standard error of the mean. (c) We found a significant correlation between region ranks in (a) and (b) of Spearman’s ρ = 0.61, p = 0.004, two-tailed. When compared with the region ranks in the discovery set, both (d) result in studies with context manipulation and (e) result in studies without context manipulation showed significant correlations of ρ = 0.92, p = 4.2 × 10−6, and ρ = 0.83, p = 4.3 × 10−7, respectively, all two-tailed.