Figure 4.
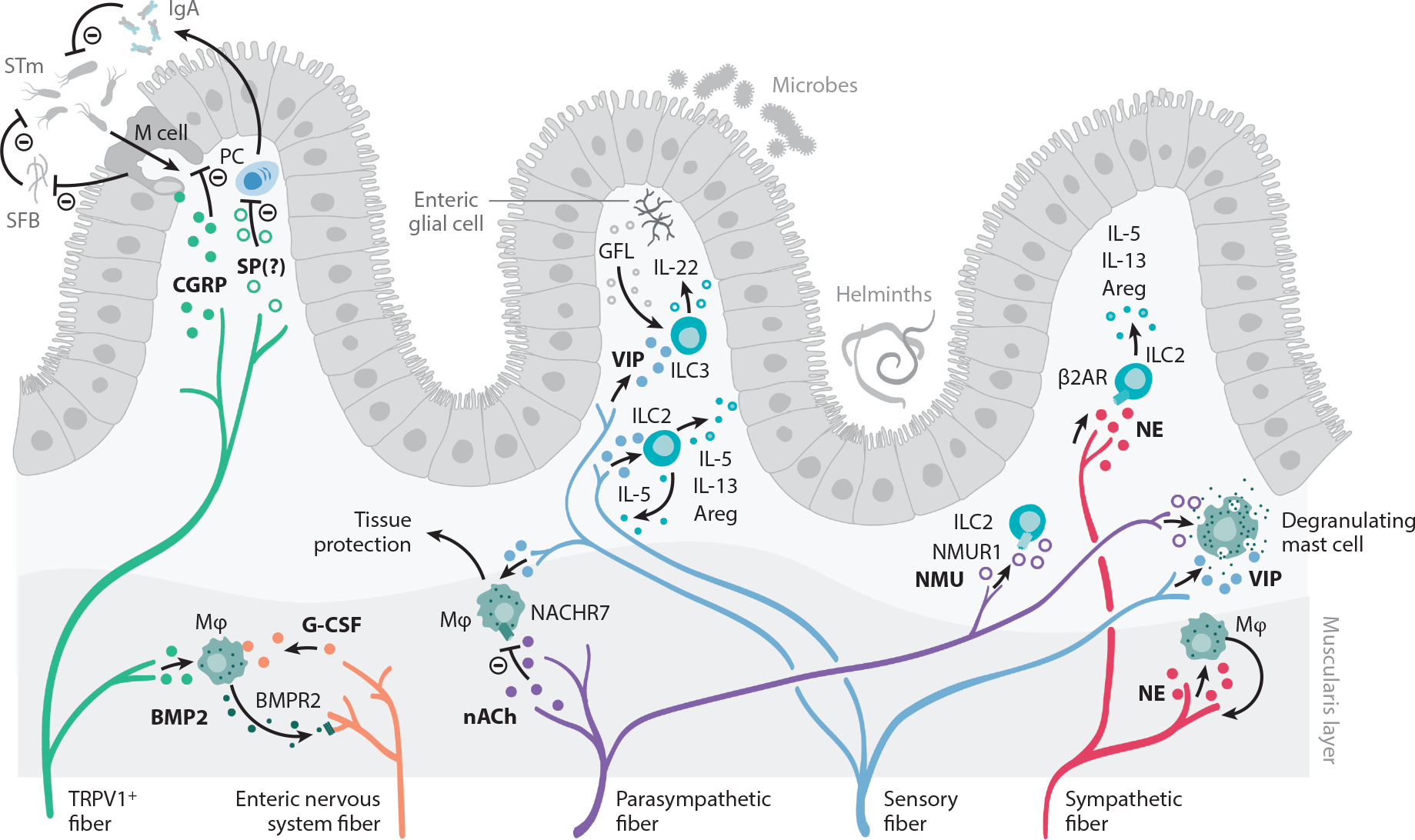
Peripheral neuroimmune interactions in the gut. The intestine is innervated by sensory fibers and the autonomic nervous system, composed of enteric neurons and sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers. Sensory afferents from vagal ganglia and lumbar-sacral DRG innervate the gastrointestinal tract and mediate protection to STm. M cells in Peyer’s patches and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue facilitate STm transfer to establish an infection. Sensing of STm by DRG TRPV1+ and Nav1.8+ fibers cause CGRP release. CGRP acts on M cells to decrease their numbers and to limit STm uptake. M cells also negatively regulate SFB density, which further antagonizes STm infection. SP may also negatively regulate immune responses to STm, as NK1R-deficient mice exhibit enhanced levels of serum IgA and increased numbers of IgA-producing cells in the lamina propria. Sensory fibers also release VIP, which acts on ILC2s and ILC3s that release type 2 cytokines and tissue-protective IL-22, respectively. ILC3s are also stimulated by the RET ligand GFL, released by enteric glial cells. Enteric nervous system fibers release G-CSF, which promotes muscularis macrophage maintenance. In turn, macrophages produce BMP2, which activates neurons via the BMPR2. Furthermore, acetylcholine acts as a negative regulator of tissue-protective muscularis macrophages via the NACHR7. NE released by sympathetic fibers promotes macrophage-induced protection of neurons during infection. The function of intestinal ILC2 is also regulated by NMU, which acts as a strong stimulator of ILC2 function, and NE, which signals through the β2AR. Finally, intestinal mast cells can integrate a wide variety of neuronal cues and respond by producing a range of inflammatory mediators, which is covered in other excellent reviews and is beyond the scope of this piece. Abbreviations: β2AR, β2 adrenergic receptor; Areg, amphiregulin; BMP2, bone morphogenetic protein 2; BMPR2, bone morphogenetic protein receptor type 2; CGRP, calcitonin gene–related peptide; DRG, dorsal root ganglia; G-CSF, granulocyte colony stimulating factor; GFL, GDNF family of ligands; IgA, immunoglobulin A; ILC2, group 2 innate lymphoid cell; ILC3, group 3 innate lymphoid cell; M, microfold; Mϕ, macrophage; NACHR7, nicotinic acetylcholine receptor 7; Nav, voltage-gated sodium channel; NE, norepinephrine; NK1R, neurokinin-1 receptor; NMU, neuromedin U; NMUR1, neuromedin U receptor; PC, Plasma cell; RET, rearranged during transfection; SFB, segmented filamentous bacteria; SP, substance P; STm, Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium; TRPV1, transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1; VIP, vasoactive intestinal peptide.
