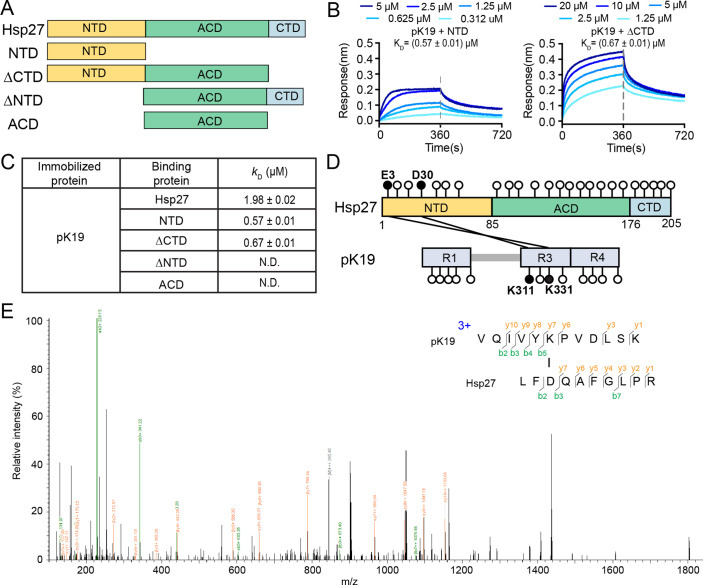
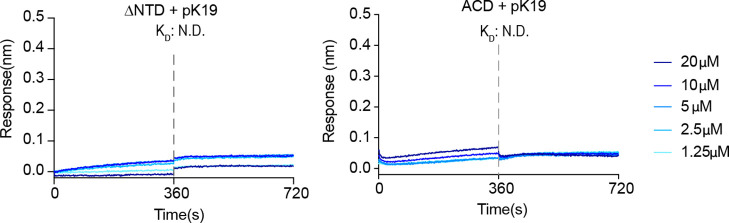
Figure 5. N-terminal domain of Hsp27 is essential in binding with pK19.
(A) Domain organization of Hsp27 and the four truncations. (B) Binding affinity of pK19 with NTD and ΔCTD of Hsp27 determined by BLI. The association and dissociation profiles were divided by a vertical dash line. pK19 was fixed to the sensor, and the 5 concentrations of Hsp27 truncations used are indicated. (C) Summary of the binding affinity of pK19 with Hsp27 wild type and truncations. (D) Schematic profile of the cross-linked results of Hsp27 to pK19 using cross-linkers EDC and NHS. All GLU (E) and ASP (D) residues in Hsp27, and all LYS (K) residues in pK19 are indicated by circles, respectively. The two identified cross-linked segments are indicated by two black lines and the corresponding residues are highlighted in black circles and labeled. (E) A representative MS/MS spectrum of trypsin proteinase-generated peptide. The m/z of fragment ions were matched to their theoretical values generated by in silico fragmentation.