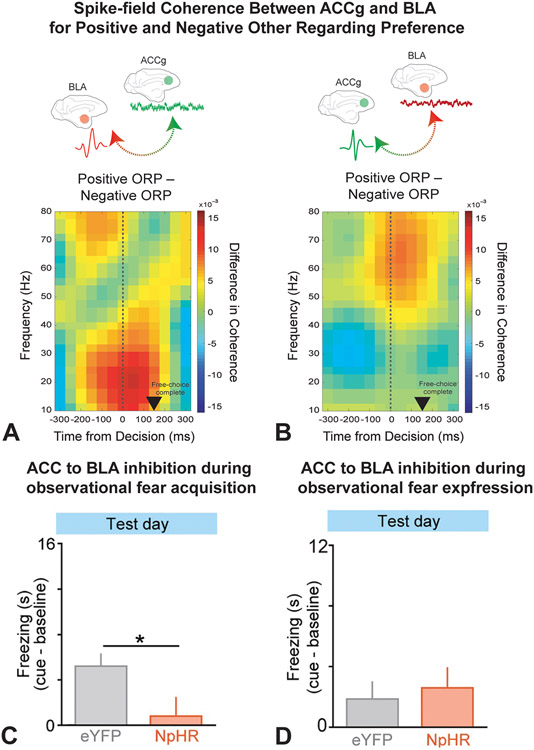
Figure 1. ACC-BLA Circuits in Social Cognition.
A–B: Dal Monte et al., 2020. A: Differences in BLA spike to ACCg LFP coherence between positive and negative ORP over time. BLA spikes and ACCg LFPs showed increased coherence in the beta frequency range for positive ORP and decreased coherence in the beta frequency band for negative ORP. B: Differences in ACCg spike to BLA LFP coherence between positive and negative ORP over time. ACCg spikes and BLA LFPs showed increased coherence in the gamma frequency range for positive ORP and decreased coherence in the gamma frequency range for negative ORP. C–D: Allsop et al., 2018. ACC→ BLA inhibition during observational fear acquisition. C: When ACC→ BLA neurons were inhibited with halorhodopsin (NpHR) during observational acquisition, NpHR mice showed significantly decreased freezing to the cue compared to control mice (eYFP) on test day. D: When ACC→ BLA neurons were inhibited with NpHR during observational fear expression, there was no significant difference between freezing behavior in control (eYFP) and NpHR mice on test day.