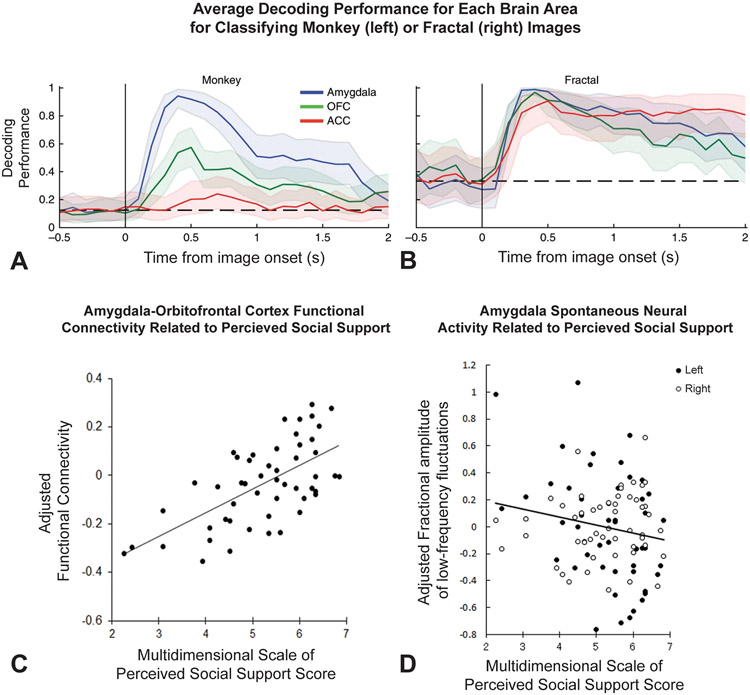
Figure 2. OFC-Amygdala Circuits in Social Cognition.
A–B: Munuera et al., 2018. To determine if neural representations of hierarchical rank and rewards associated with fractal images were encoded by overlapping neuronal populations, the researchers trained a linear decoder to distinguish between fractal trials with either a large reward or no reward. The decoder was then tested on held-out trials of the same type and trials in which monkeys viewed two images of monkey faces. A: Depicts the average decoding performance for Amygdala, OFC, and ACC for distinguishing between trials in which hierarchical rank of the two monkey face images presented differed. Decoding performance on monkey face trials was greater in the amygdala than in the OFC or ACC. B: Depicts the average decoding performance for Amygdala, OFC, and ACC for classifying fractal images. Decoding performance on held-out fractal trials was high for all three regions. C–D: Sato et al., 2020 C: Left amygdala to right OFC functional connectivity was positively correlated with Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support (MSPSS) scores. D: Bilateral amygdala fractional amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations (fALFF) values were negatively correlated with MSPSS scores.