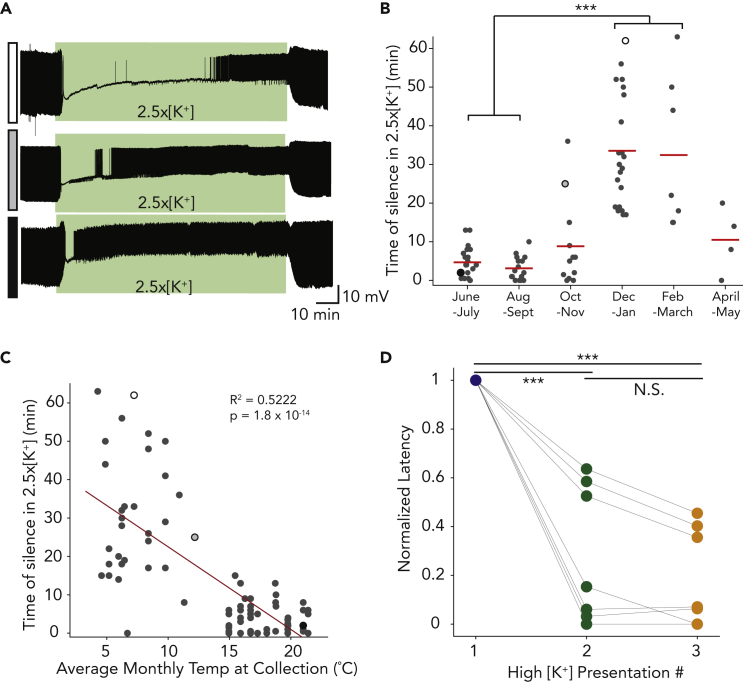
Figure 6.
Robustness to high potassium saline varies along with the time of year and local seawater temperatures
(A) Representative traces from three PD neurons with different robustness to a 90-min application of high potassium saline (green boxes).
(B) Time of each PD neuron’s silence in high potassium saline grouped by month of crab collection (N = 82). Red lines indicate the mean time of silence for each two-month bin.
(C) Visualization of the same data shown in (B), with each PD neuron’s time of silence in high potassium saline plotted against the average surface seawater temperature during the month the crabs were collected. Black outlined dots in (B) and (C) correspond to the traces shown in (A), pattern code in left-hand boxes. Temperature data were compiled from NOAA (https://www.ndbc.noaa.gov/station_history.php?station=44013). ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(D) Normalized latency to first spike averaged for each preparation to the latency in the first high potassium application, re-analyzed data from Figure 2. Normalized latency to recovery of the first action potential for each PD neuron across three high potassium perturbations. The time of silence in the first application is significantly higher than the second (∗∗∗p = 1.75 x 10−6) and third applications (∗∗∗p = 1.55 x 10−6).