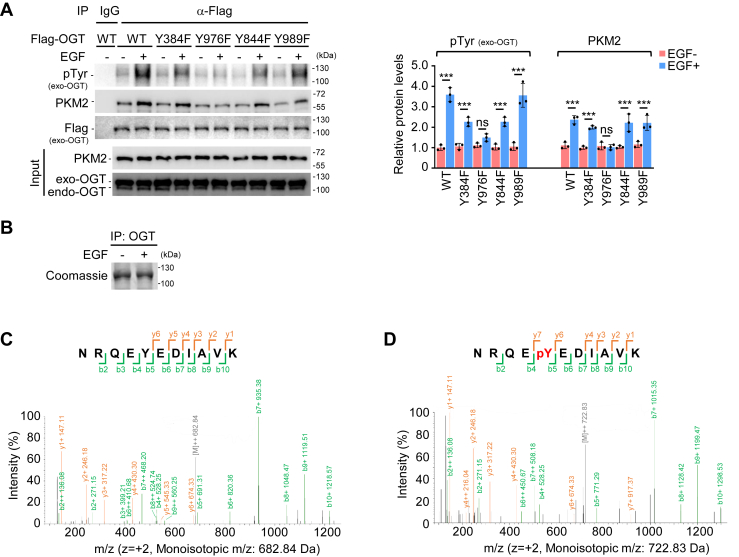
Figure 3.
EGF signal triggers OGT Y976 phosphorylation.A, mutation at OGT Y976 abolishes PKM2 binding. (left) Transfection of Flag-tagged OGTWT, OGTY384F, OGTY976F, OGTY844F, or OGTY989F along with or without concomitant EGF treatment (100 ng/ml for 1 h) was conducted in A549 cells. OGT-associated proteins were immunoprecipitated and analyzed by WB. Exo, exogenous; endo, endogenous. (right) Relative protein levels of IP. OGT pTyr and PKM2 were normalized to Flag (exo-OGT). Quantification shows mean ± SD (n = 3) with significance determined by two-way ANOVA, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ns, nonsignificant. B–D, analysis of OGT Y976 phosphorylation by mass spectrometry. A549 cells treated with or without EGF (100 ng/ml) for 1 h were harvested and prepared for IP with OGT antibody prior to mass spectrometry (MS) analysis. B, examination of purified OGT proteins. Endogenous OGT were isolated by IP, separated by SDS-PAGE, and stained with Coomassie blue. C and D, evaluation of OGT phosphorylation. Purified OGT proteins were trypsinized prior to MS analysis. The data were processed with the MASCOT engine, which identified the peptides NRQEYEDIAVK (C, EGF untreated, m/z = 682.84 Da) and NRQEpYEDIAVK (D, EGF treated, m/z = 722.83 Da). The y and b fragmentations were used to map the phosphorylation site to the Tyr indicated in red. EGF, epidermal growth factor; EGFR, EGF receptor; IP, immunoprecipitation; WB, western blotting.