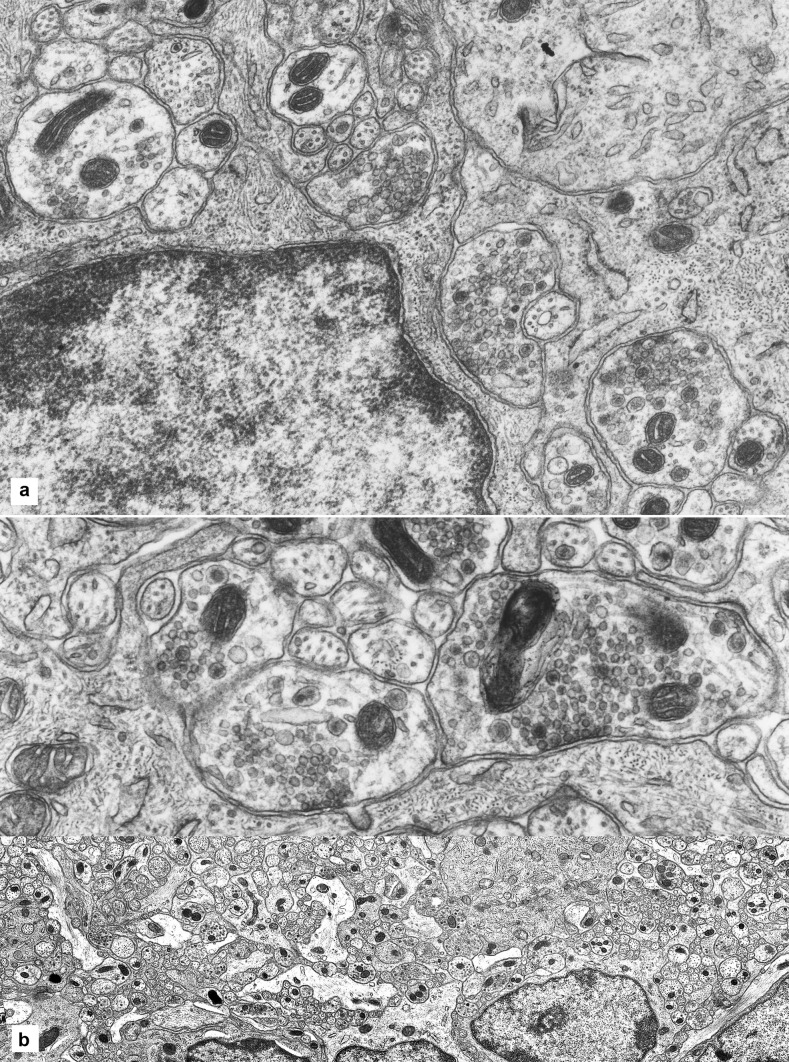
Fig. 4.
Axon-glia contacts. A A glial cell, with its nucleus, occupying the bottom left quarter of the picture, and one of its processes at centre have two large vesicle-studded axons abutting on them (circled). Another axon-glial contact is visible on the glial cell at the right (circled) and one at the far left (circled). The four axons (nerve endings or varicosities) show vesicles aggregating against a membrane density; no specialized structures appear on the glial side of these contacts. Width of the microscopic field: 9 µm. B A long glial process issuing from a cell body, to the left, is contacted by two large nerve endings (varicosities) mainly occupied by mitochondria and vesicles; the latter are clustered under a membrane density that is visually identical to those found in synapses. No structural specializations are visible on the glial side. Width of the microscopic field: 6.5 µm