FIGURE 2.
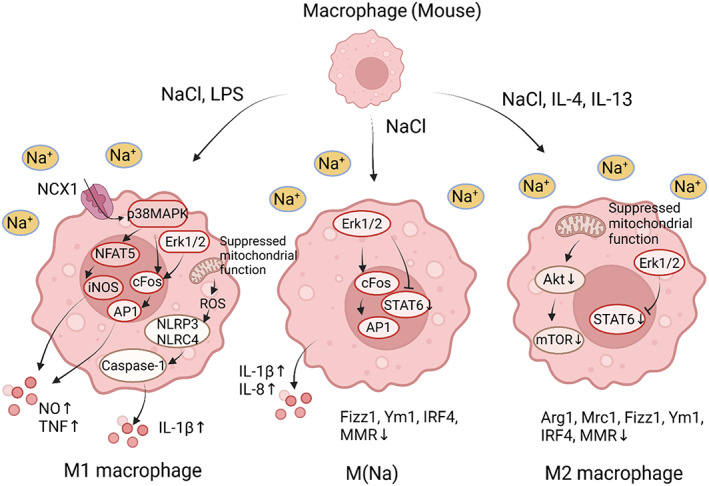
High salt induces a pro‐inflammatory profile in murine macrophages. NCX1 expressed on M1 macrophages can sense extracellular Na+, and high salt increases NO and TNF production by p38/MAPK‐dependent NFAT5 activation and downstream iNOS upregulation. Moreover, high salt activates NLRP3 and NLRC4 inflammasomes via mitochondrial ROS, thereby increasing IL‐1β in a caspase‐1‐dependent manner. Additionally, high salt induces a pro‐inflammatory profile in M1 and M(Na) macrophages through the p38/cFos/AP1 and Erk1/2/cFos/AP1 pathways, whereas the Erk1/2/STAT6 pathway mediates the salt‐driven suppression of M2 and M(Na) macrophages. In M2 macrophages, high salt downregulates the expression of Arg1, mannose receptor, C type 1 (Mrc1), inflammatory zone 1 (Fizz1), chitinase‐like 3 (Chil3 or Ym1), interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) and macrophage mannose receptor (MMR). Furthermore, high salt suppresses mitochondrial metabolism and AKT/mTOR signalling in M2 macrophages. The mitochondrial function of M1 macrophages is also suppressed by high salt.
