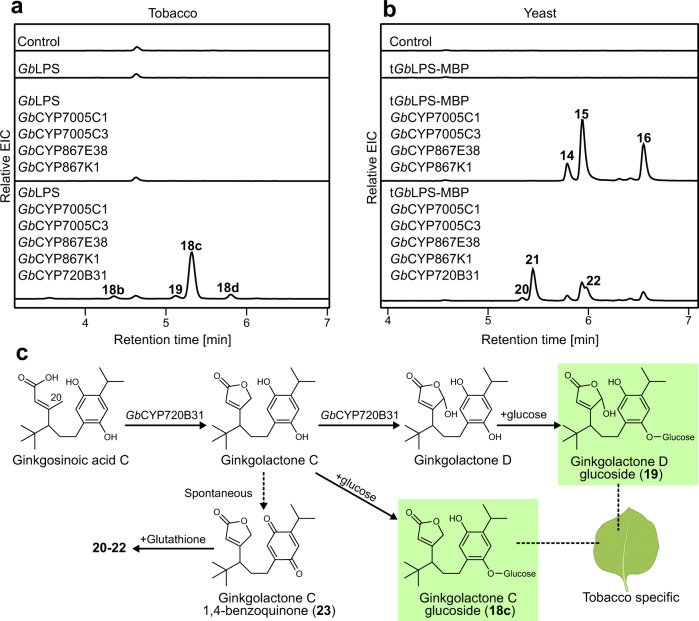
Fig. 4. The first lactone ring towards ginkgolide biosynthesis is generated from the activity of GbCYP720B31.
a LC–HRMS analysis of tobacco leaf extracts expressing GbLPS and the combinations of CYP candidates are shown in the panel. The chromatograms shown are EICs (positive mode) for the m/z values of 333.2062 and 331.1904, each with a window of ±0.05. b LC–HRMS analysis of yeast terpenoids extracts from strains expressing SpGGPPS7, SctHMGR, GbLPS, GbPOR2 and the combinations of CYP candidates shown in the panel. The chromatograms shown are extracted ion chromatograms (EICs, positive mode) for the m/z values 636.2581; 638.2751, and 640.2890, each with a window of ±0.05. c Proposed biosynthetic steps from ginkgosinoic acid C to ginkgolactone C and D derivatives, likely catalyzed by GbCYP720B31. The chemical structures of the compounds shown here (18c, 19, and 23) were structurally elucidated using NMR spectroscopy. The putative intermediates ginkgolactone C and D were not detected in their free form but only as glucosides (18c and 19) from tobacco, or in conjugation with glutathione (20–22). Enzymatic in vitro removal of the glucose moiety from 18c gave rise to 23, a 1,4 benzoquinone derivative of ginkgolactone A (Supplementary Fig. 9b). The numbering of carbon atoms follows the standard numbering of levopimaradiene. The Nicotiana benthamiana leaf image has been created by BioRender.com (2021).