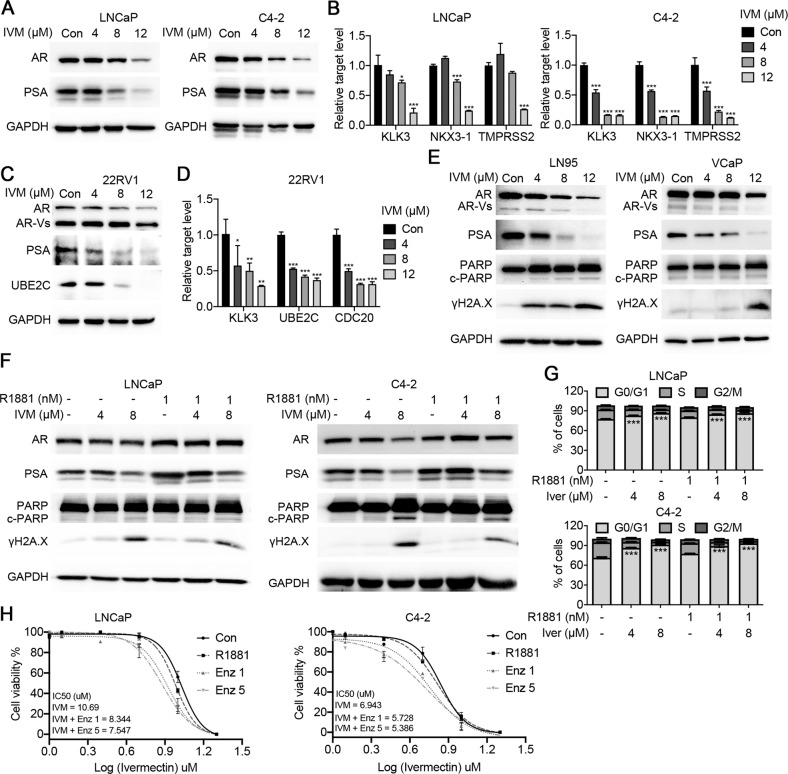
Fig. 3. Ivermectin inhibited the FL-AR and AR-V7 signaling activity.
A Western blot analysis of AR and PSA in LNCaP and C4-2 cells treated with ivermectin for 48 h. B RT-qPCR analysis of AR target genes (KLK3, TMPRSS2, and NKX3-1) in LNCaP and C4-2 cells treated with ivermectin for 48 h. C Western blot analysis of FL-AR, ARVs, PSA, and UBE2C in ivermectin-treated 22RV1 cells at 48 h. D RT-qPCR analysis of KLK3 and ARV target genes (UBE2C and CDC20) in 22RV1 cells treated with ivermectin for 48 h. E Western blot analysis of FL-AR, ARVs, PSA, PARP, and γH2A.X in the other two ARV-positive cells lines, LN95 and VCaP, treated with ivermectin for 48 h. F Western blot analysis of AR, PSA, PARP, and γH2A.X in LNCaP and C4-2 cells after the implementation of 4 μM and 8 μM of ivermectin with or without 1 nM R1881. G Ivermectin inhibited the cell cycle at G0/G1 in the presence of R1881. LNCaP and C4-2 cells were treated with ivermectin at 4 and 8 μM for 48 h in the absence or presence of 1 nM R1881. H Cell viability was measured by the MTT assay. LNCaP and C4-2 cells were treated with indicated concentrations of ivermectin for 48 h with or without 5 μM and 10 μM enzalutamide for 48 h.