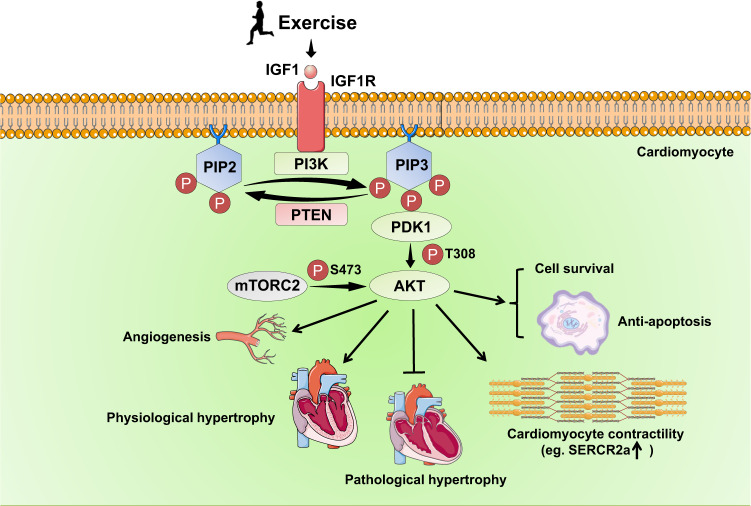
Fig. 2.
The IGF1/PI3K/AKT pathway in exercise-induced physiological cardiac hypertrophy and exercise-induced cardioprotection. Exercise induces IGF1 secretion, which activates IGF1R tyrosine kinase followed by recruitment of PI3K. The PI3K through converting PIP2 to PIP3 in the plasma membrane, further leads to recruitment of PDK1 and AKT to the plasma membrane and subsequent phosphorylation and activation of PDK1 and AKT. The activation of IGF1/PI3K/AKT is essential to mediate exercise-induced physiological cardiac hypertrophy through promoting cardiomyocyte growth in size. The IGF1/PI3K/AKT pathway also exerts cardioprotective effects through promoting cardiomyocyte contractility, enhancing survival while reducing apoptosis of cardiomyocytes, inhibiting pathological hypertrophy, and promoting angiogenesis. IGF1 insulin growth factor 1, IGFR1 insulin growth factor 1 receptor, PI3K phosphoinositide-3 kinase, PIP2 phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, PIP3 phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate, PDK1 phosphoinositide dependent kinase 1, AKT protein kinase B, PTEN phosphatase and tensin homolog, mTORC2 mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2, SERCA2a sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase 2a