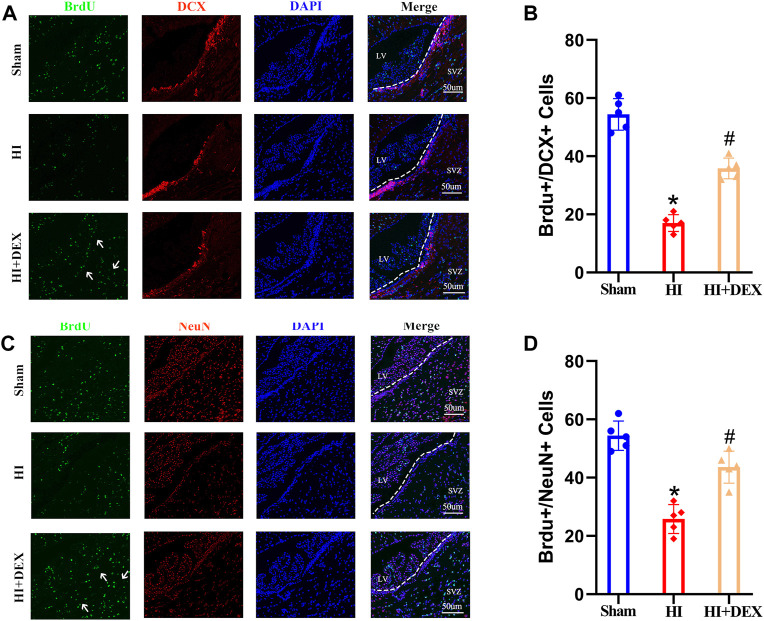
FIGURE 3.
DEX promoted neurogenesis in the SVZ after HIBD. Neonatal HIBD was induced in rats on PND7. DEX (25 μg/kg) was administered directly by intraperitoneal injection after the onset of HIBD. BrdU was administered daily for three consecutive days starting on day 4 (D4). Rats in the sham group, HI group and HI + DEX group were trans-cardially perfused with paraformaldehyde and brain sections were taken on D14 and D28. The brain sections on D14 were double labeled with anti-BrdU (green) and anti-DCX (red) antibodies to detect newly formed neuroblasts. The brain sections on D28 were double labeled with anti-BrdU (green) and anti-NeuN (red) antibodies to detect newly formed neurons. (A,B) Representative images were captured using a laser scanning confocal microscope (magnification ×400, scale bar: 50 μm). The white arrows highlight a significant increase in the number of positive cells. (C,D) Statistical analysis of double-positive cells showed that the newly formed neuroblasts and newly formed neurons were significantly reduced in the SVZ of the ipsilateral injured hemisphere in neonatal rats caused by HIBD. This phenomenon was significantly reversed by DEX. DEX, Dexmedetomidine; SVZ, Subventricular zone; LV, Lateral ventricle; HIBD, hypoxic-ischemic brain damage; PND7, Postnatal day 7; D4, D14, D28: 4, 14, 28 Day after HIBD; HI, hypoxic-ischemia; The data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 5 per group). *p < 0.05 vs. the sham group; # p < 0.05 vs. the HI group.