FIGURE 5.
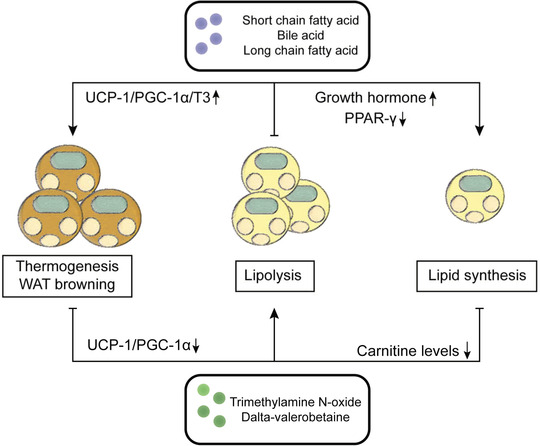
Metabolites affect adipose tissue function. Under the action of beneficial metabolites (short‐chain fatty acids [SCFAs], bile acids [BAs], long‐chain fatty acids [LCFAs]), adipose tissue promotes adipose thermogenesis and browning through uncoupling protein 1 (UCP‐1)/peroxisome proliferator‐activated receptor gamma‐coactivator 1α (PGC‐1α)/T3, promotes adipose decomposition through growth hormones produced by metabolites in the brain to balance energy metabolism in adipose tissue. In contrast, metabolites (trimethylamine N‐oxide [TMAO] and delta‐valerobetaine [VB]) inhibit browning and thermogenesis of adipose tissue, reduce lipid decomposition by reducing carnitine levels, and promote infiltration of immune cells and proinflammatory cytokines.
