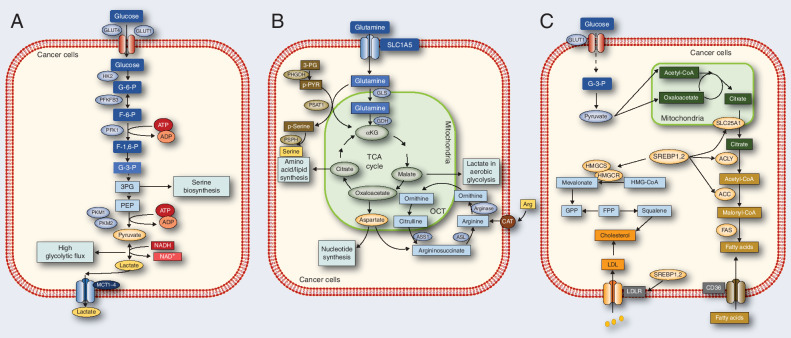
Figure 1.
Reprogrammed metabolic activities in cancer. A, The flux of glucose metabolism and glycolysis is accelerated in cancer cells by preferential expression of transporters and irreversible enzymes that drive glucose flux forward and satisfy the anabolic demands of cancer cells. Transporters and enzymes that are predominant in cancer cells are shown in red. B, Cancer cells rely on the exogenous supply of Arg and are regulated by arginase, ASL, and ASS1. Glutamine can be converted by GLS and GDH. The serine synthesis pathway utilizes the glycolytic intermediate 3P-glycerate, which is converted by PHGDH, PSAT-1, and PSPH into serine. Enzymes that are predominant in cancer cells are shown in red. C, In cancer cells, glucose uptake and glycolysis are markedly upregulated, generating large amounts of pyruvate. Pyruvate is converted to citrate in mitochondria, which is transported by SLC25A1 from the mitochondria into the cytoplasm. The citrate serves as a precursor for de novo synthesis of fatty acids and cholesterol in the cytoplasm. Acetate is converted to acetyl-CoA by the ACSS2 enzyme, serving as another source of lipid synthesis. Related enzymes upregulation promotes fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis, while the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) and CD36 upregulation increase fatty acid and cholesterol uptake.