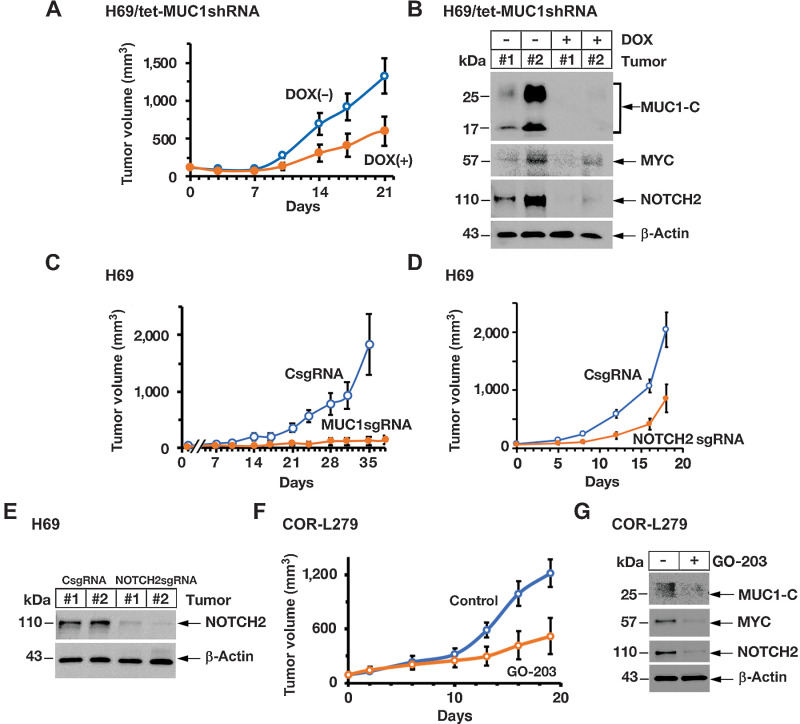
Figure 6.
Targeting MUC1-C suppresses SCLC tumorigenicity. A, Six-week old nude mice were injected subcutaneously in the flank with 1 × 106 H69/tet-MUC1shRNA cells. Mice were pair-matched into two groups when tumors reached 100 to 150 mm3 and were fed without and with DOX. Tumor volumes are expressed as the mean ± SD for 6 mice. B, Lysates from two untreated and two DOX-treated H69/tet-MUC1shRNA tumors obtained on day 21 were immunoblotted with antibodies against the indicated proteins. C, Six-week-old nude mice were injected subcutaneously in the flank with 1 × 106 H69/CsgRNA and H69/MUC1sgRNA cells. Tumor volumes are expressed as the mean ± SD for 6 mice. D, Six-week-old nude mice were injected subcutaneously in the flank with 1 × 106 H69/CsgRNA and H69/NOTCH2sgRNA cells. Tumor volumes are expressed as the mean ± SD for 6 mice. E, Lysates from two H69/CsgRNA and two H69/NOTCH2sgRNA tumors obtained on day 18 were immunoblotted with antibodies against the indicated proteins. F and G, Six-week-old nude mice were injected subcutaneously in the flank with 3 × 106 COR-L279 cells. Mice pair-matched into two groups when tumors reached 100 to 150 mm3 were treated intraperitoneally each day with PBS or GO-203 for 19 days. Tumor volumes are expressed as the mean ± SEM for 6 mice (F). Lysates from tumors harvested on day 19 were immunoblotted with antibodies against the indicated proteins (G).