Figure 5. Erlins interact with RHBDL4 and MHC202.
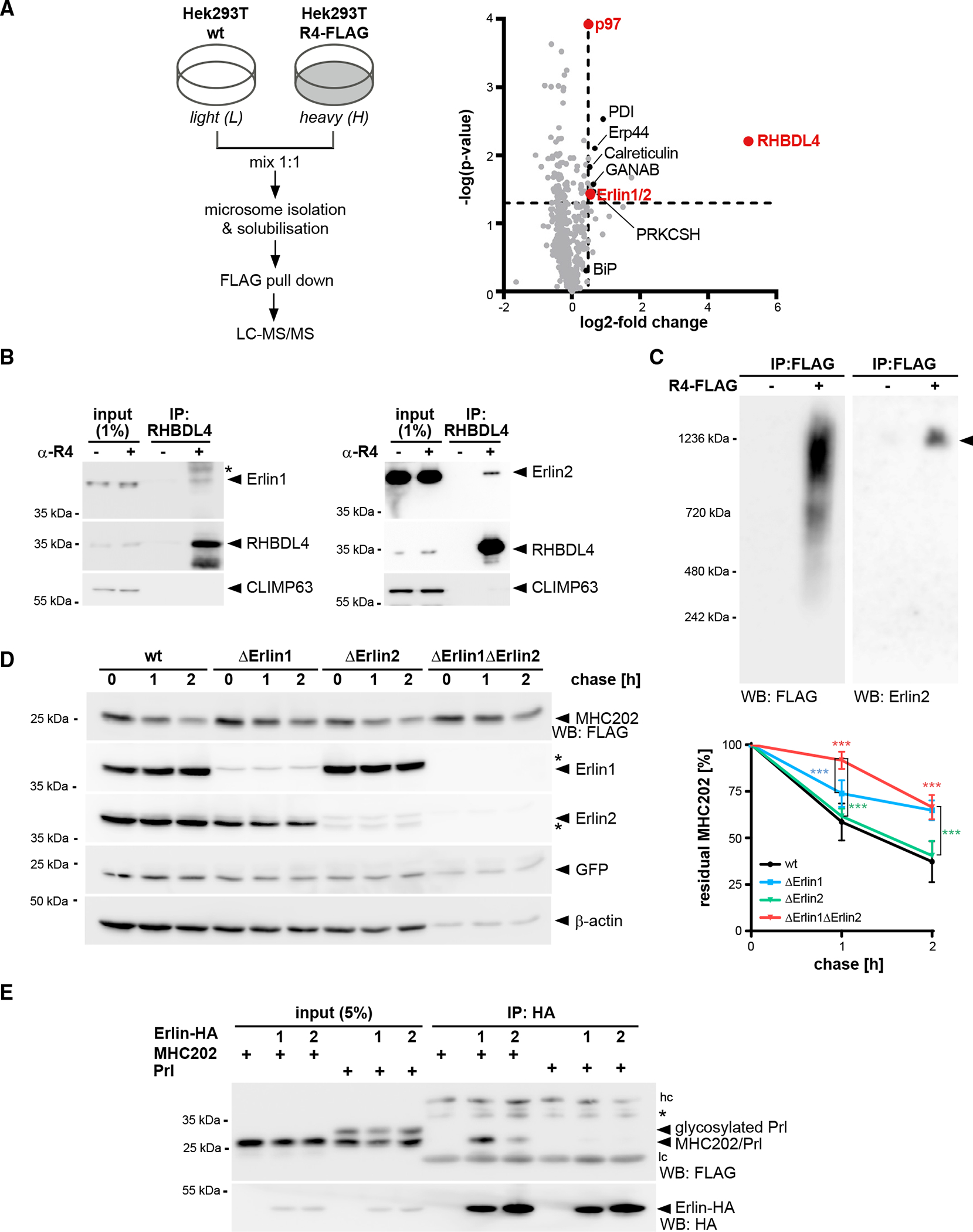
(A) SILAC-based mass spectrometry analysis of RHBDL4 interactome from Triton X-100-solubilized microsomes obtained from Hek293T cells with chromosomally FLAG-tagged RHBDL4 (Hek293T R4-FLAG) was performed as outlined. Volcano plot shows a representation of potential RHBDL4 interaction partners identified in all three replicates.
(B) Endogenous RHBDL4 was isolated by immunoprecipitation (IP). Western blotting (WB) identifies co-purification of endogenous Erlin1 and Erlin2. CLIMP63 was used as a negative control. Asterisk, non-specific band.
(C) Ectopically expressed RHBDL4-FLAG formed several higher-molecular-weight complexes in addition to the 1.2-MDa complex containing Erlin2 (filled triangle).
(D) MHC202 degradation is delayed in Erlin1 Hek293T knockout cells (ΔErlin1) compared with Hek293T WT cells (wt), as shown by cycloheximide (CHX) chase. To block potential compensation by ER-phagy, cells were pre-treated with 100 nM BafA1 for 3 h. In Erlin1/Erlin2 Hek293T double-knockout cells (ΔErlin1ΔErlin2), MHC202 is significantly stabilized. To ensure homogeneous expression of MHC202 within each cell line, GFP expressed from a downstream internal ribosome entry site (IRES) and endogenous β-actin were used as controls. Asterisks indicate cross-reacting Erlin1 and Erlin2 signals. Quantification of four independent experiments is shown on the right (means ± SEM, n = 4, ***p ≤ 0.001, two-way ANOVA).
(E) HA-tagged Erlin1 (1) and Erlin2 (2) specifically interact with MHC202 but not with Prl. hc, heavy chain; lc, light chain; asterisk, non-specific band.
For (B)–(E), representative experiments of three or four biological replicates are shown.
