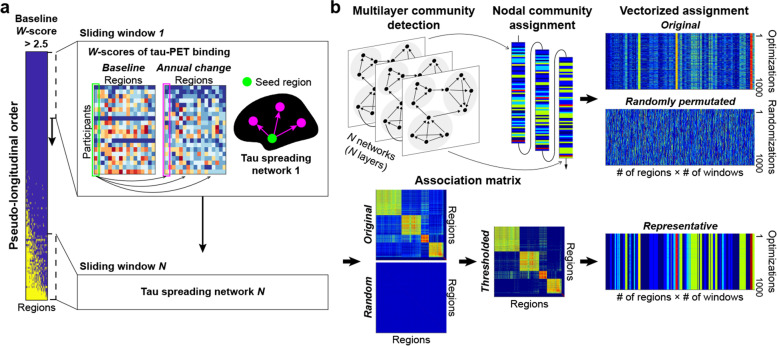
Fig. 1.
Study overview. a All individuals in each age group were sorted by the extent of baseline tau burden to present a pseudo-longitudinal order of disease progression. For all subjects involved in each window moving across the pseudo-longitudinal order, DTGR approach was applied between baseline W-scores of a seed region and annual changes in W-score of another region to construct a tau spreading network. b We optimized community structures by maximizing a modularity function, considering internetwork connections between the consecutive tau spreading networks. Due to the heuristic nature of the optimization algorithm, the optimization process was repeated 1000 times and every single node of each network was assigned a community at each iteration. A regional association matrix was then constructed from 1000 original assignments and 1000 randomly permuted assignments, respectively. The original association matrix was thresholded by a maximum value of the random association matrix, and a representative assignment was determined by applying community detection algorithm to the thresholded association matrix