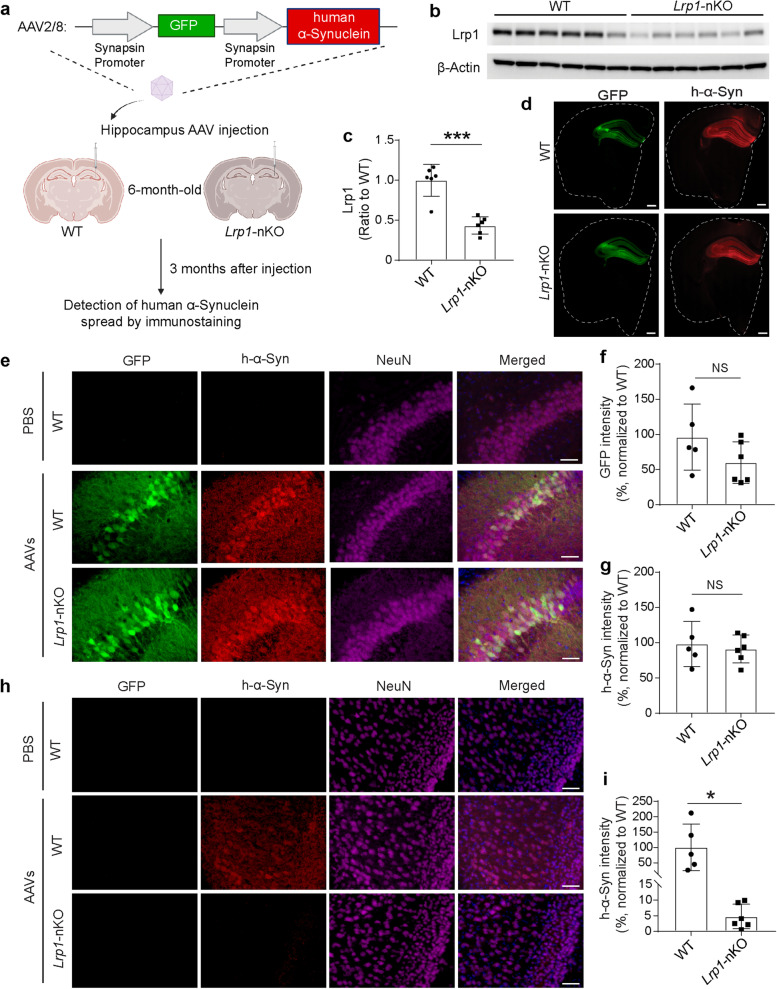
Fig. 4.
Neuronal Lrp1 knockout reduces α-Syn spread in vivo. a Schematic drawing for the stereotactic injection of AAV-synapsin-GFP-synapsin-h-α-Synuclein into the neuronal Lrp1 knockout (Lrp1-nKO) mice and wild type (WT) littermate controls, and the experimental workflow. b and c, Western blotting showing the endogenous Lrp1 protein in the cortex of WT (n = 6) and Lrp1-nKO mice (n = 6). d Representative sections showing GFP and h-α-Syn signals in mouse brains. Dotted line marks the outline of each section. Scale bars, 500 μm. e Representative images showing GFP and h-α-Syn signals in the hippocampus region from WT and Lrp1-nKO mice. Scale bars, 50 μm. f Quantitative analysis of GFP intensity in hippocampus from WT or Lrp1-nKO mice. g Quantitative analysis of h-α-Syn immunofluorescence intensity in hippocampus from WT or Lrp1-nKO mice. h Representative images showing h-α-Syn spreading to the cortex region from WT or Lrp1-nKO mice. Scale bars, 50 μm. i Quantitative analysis of h-α-Syn immunofluorescence intensity in the cortex from WT or Lrp1-nKO mice. Experiments in (e–i) n = 5 mice (3 males and 2 females) for WT and n = 6 mice (3 males and 3 females) for Lrp1-nKO mice. All data are expressed as mean ± s.d. with individual data points shown. Data were analyzed by unpaired two-sided t-test. NS, not significant; *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001