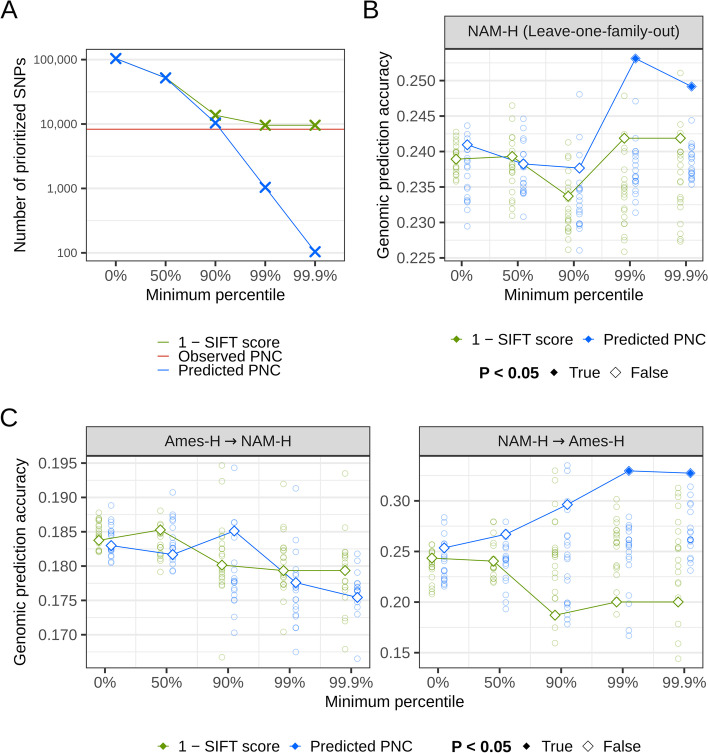
Fig. 7.
Prioritization of nonsynonymous SNPs in genomic prediction for grain yield, in hybrid maize lines. A Number of SNPs prioritized by SIFT conservation (1 − SIFT score), predicted phylogenetic nucleotide conservation (PNC), or observed PNC. B Genomic prediction accuracy within panel, in leave-one-family-out prediction in the Nested Association Mapping hybrid panel (NAM-H) [16]. C Genomic prediction accuracy across panels, from a diverse hybrid panel (Ames-H) to NAM-H, and vice versa [16]. Genomic prediction models included effects of population structure variables (top three principal components in the Hapmap 3.2.1 reference panel in maize), effects of genome-wide SNPs, and effects of nonsynonymous SNPs. Diamonds: nonsynonymous SNPs were weighted by SIFT conservation or predicted PNC, and prioritized by truncating weights to zero if they were under the 0%, 50%, 90%, 99%, or 99.9% percentile. Open circles: nonsynonymous SNPs were weighted and prioritized by 20 random permutations of SIFT conservation or predicted PNC, to determine whether the prediction accuracy by SNP weights was significantly different from the accuracy by random SNP weights