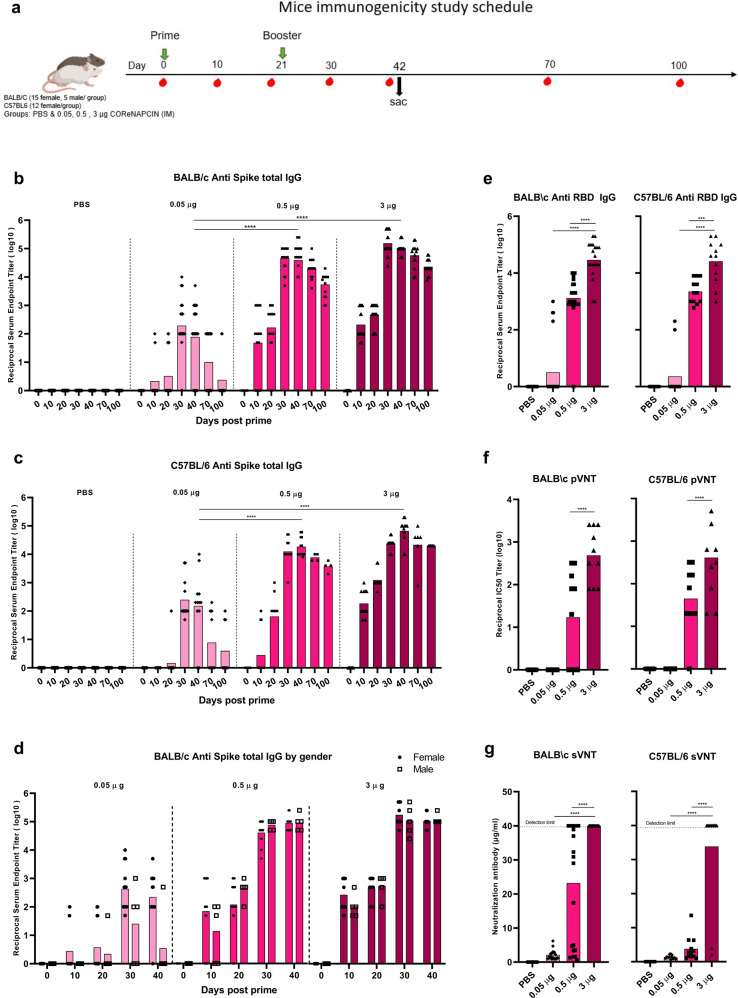
Fig. 2. Induction of potent and persistent antibody response with robust neutralizing capacity by COReNAPCIN®.
a BALB/c (n = 20 each group) and C57BL/6 mice (n = 12 each group) were i.m. injected with 0.05 (light pink), 0.5 (pink) or 3 µg (purple) COReNAPCIN® at day 0 and day 21. Animals in the control group received PBS injection (gray). b–d Sera were collected before and at different days post prime and tested for SARS-CoV-2 Spike-specific total IgG by ELISA. In (d), the anti-S IgG specific binding antibody endpoint titer of five different time points in male and female BALB/c is compared. e–g The sera of day 40 post prime were assessed for anti-RBD IgG binding antibody using ELISA (e), for neutralizing capacity against pseudotype SARS-CoV-2 using pVNT (f) and for ACE2 binding inhibition ability using sVNT (g). Each data point is shown, the height of each bar represents the geometric mean. All statistical analyses were performed using one-way ANOVA followed by multiple comparisons Dunn’s post-hoc test. A p value less than 0.05 (***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001) was assumed to be statistically significant.