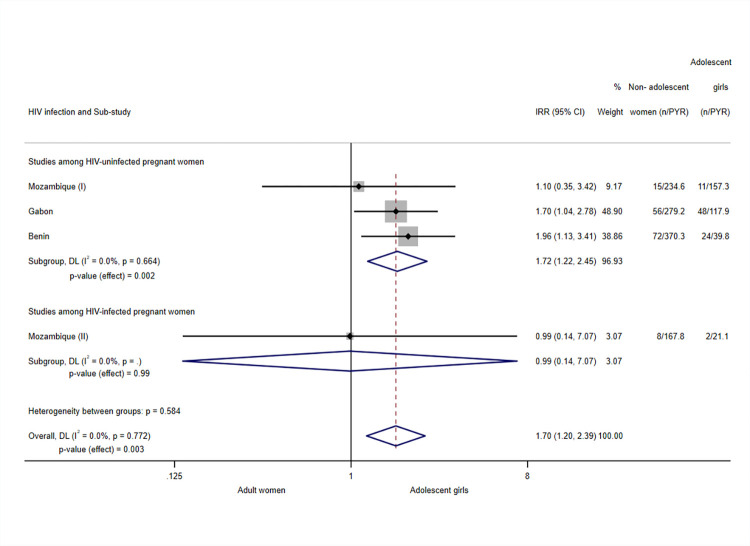
Fig 1. Analysis for clinical malaria episodes during pregnancy.
Notes: Analyses adjusted by trial arm, gravidity, literacy, gestational age at recruitment, MUAC, anaemia at recruitment, adherence to the treatment (IPTp), and season at recruitment. Weights and between-subgroup heterogeneity test are from random-effects model. Tanzania (I), HIV-uninfected participants, and Tanzania (II), HIV-infected participants, were excluded from the analysis since no clinical malaria cases were reported in the study site. Kenya was excluded as well from the analysis because no clinical malaria episodes were reported among adolescent girls and no statistical adjustment could be applied to allow its inclusion. CI, confidence interval; DL, DerSimonian–Laird random effects model; IRR, incidence risk ratio; MUAC, mid-upper arm circumference; PYR, person-years at risk.