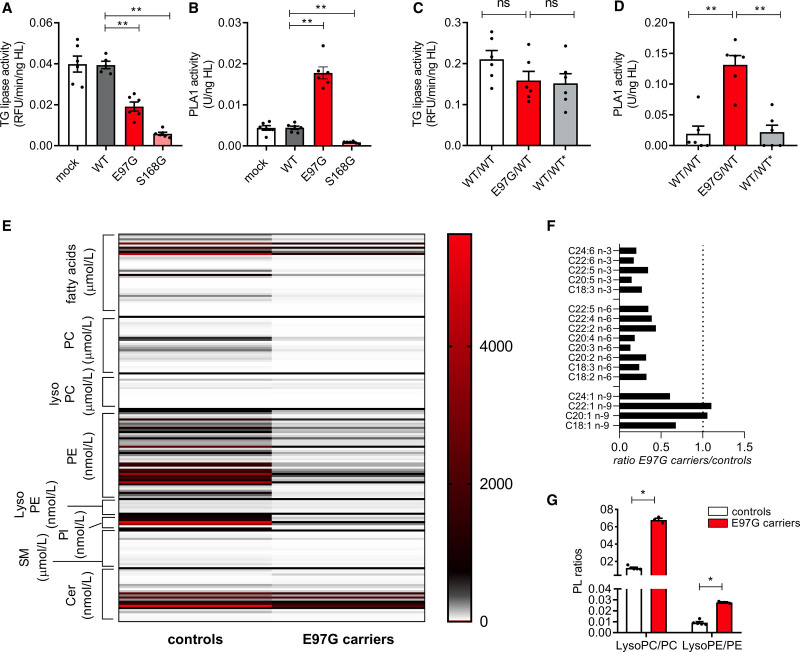
Figure 4.
E97G alters hepatic lipase substrate specificity. A and B, Triglyceride (TG) lipase activity and phospholipase A1 (PLA1) activity in medium of heparin-treated immortalized human hepatocytes with overexpression of wild-type LIPC (LIPC-WT), LIPC-E97G, or LIPC-S168G. C and D, Triglyceride lipase activity and PLA1 activity in medium of heparin-treated immortalized human hepatocytes with a wild-type allele, a heterozygous presence of the E97G variant, or a corrected wild-type allele. Each enzymatic activity was corrected for the amount of released hepatic lipase (HL). E, Lipidomics data of plasma of control individuals (n=5) or E97G carriers (n=3). Values are depicted in nanomoles per liter (phosphatidylethanolamine [PE], lysophosphatidylethanolamine [LysoPE], phosphatidylinositol [PI], ceramides [Cer]) or micromoles per liter (fatty acids [FAs], phosphatidylcholine [PC], lysophosphatidylcholine [LysoPC], sphingomyelin [SM]). F, Ratios of plasma FA levels between control individuals (n=5) and E97G carriers (n=3). G, Phospholipid (PL) ratios of lysophospholipids/phospholipids in control individuals (n=5) or family members (n=3). Cell culture data are of 3 independent experiments with a technical duplicate. Statistical significance determined by Mann-Whitney tests. ns Indicates not significant; and RFU, relative fluorescence units. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001.