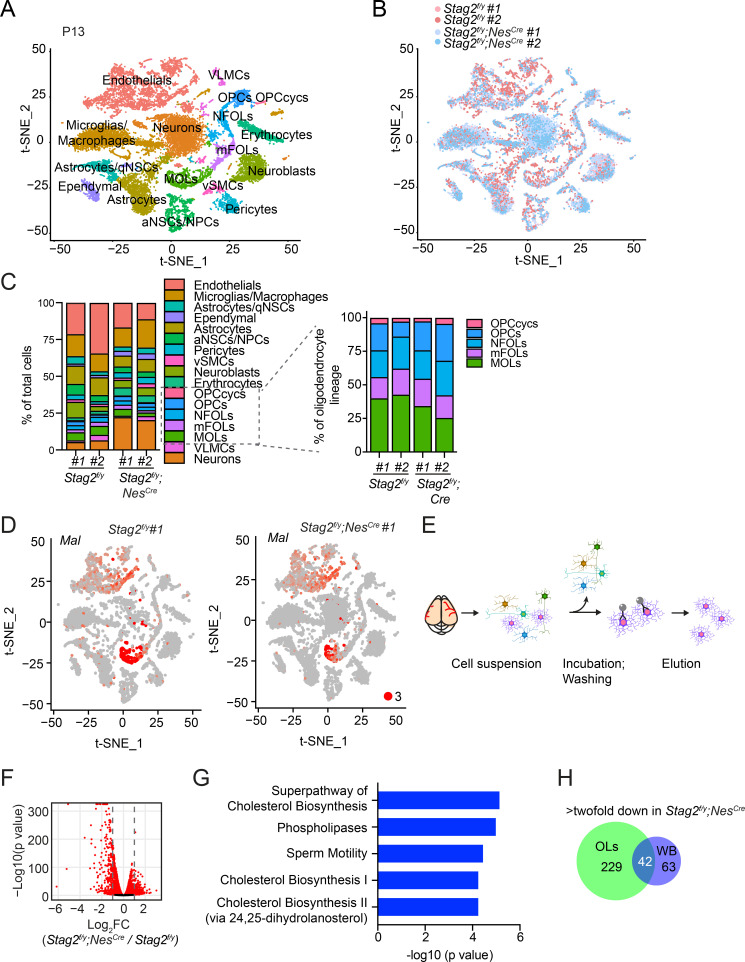
Figure 4. Deletion of Stag2 in mouse brains causes differentiation delay and transcriptional changes in oligodendrocytes.
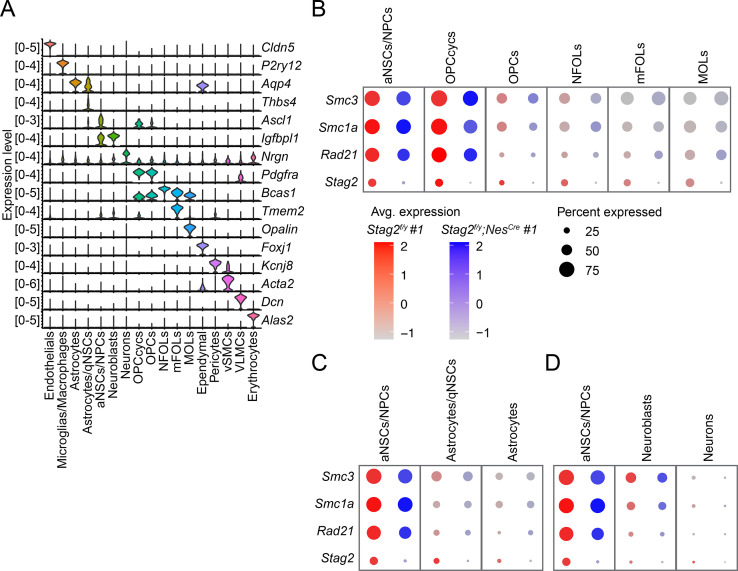
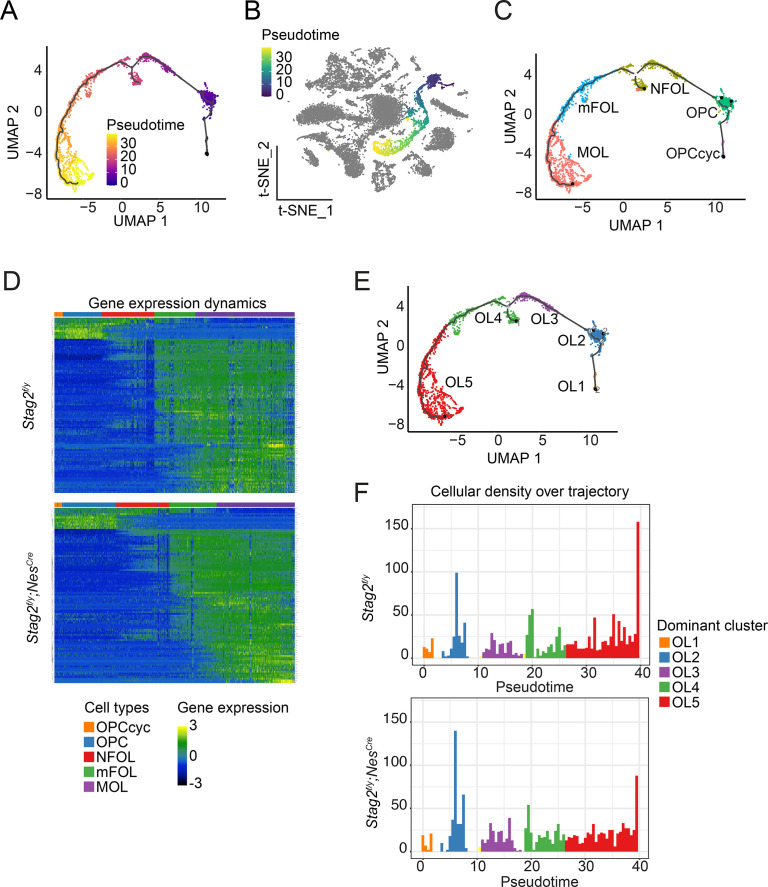
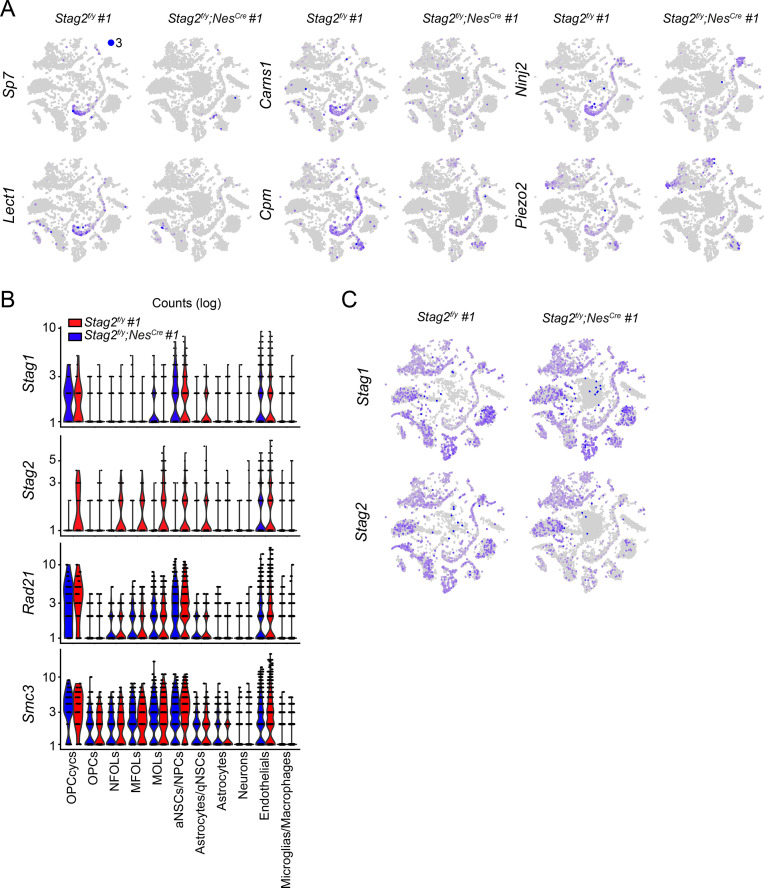
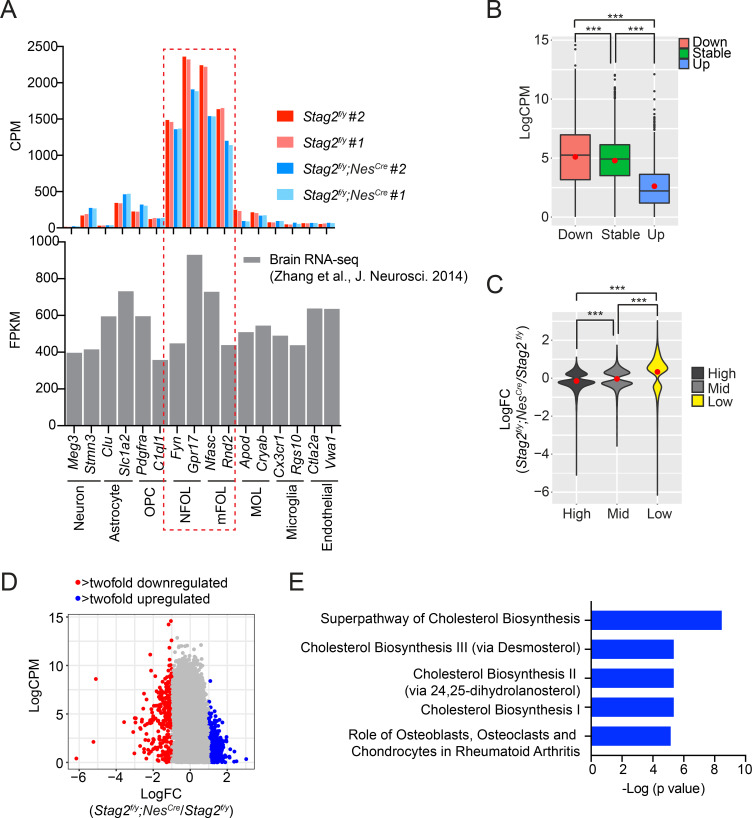
(A) t-SNE plot of cell clusters in Stag2f/y and Stag2f/y;NesCre forebrains analyzed by single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq). n = 2 mice of each genotype were used in the scRNA-seq analysis. aNSCs/NPCs, active neural stem cells or neural progenitor cells; Astrocytes/qNSCs, astrocytes or quiescent neural stem cells; OPCcycs, cycling oligodendrocyte (OL) progenitor cells; OPCs, OL progenitor cells; NFOLs, newly formed OLs; mFOLs, myelin-forming OLs; MOLs, matured OLs; VLMCs, vascular and leptomeningeal cells; vSMCs, vascular smooth muscle cells. (B) t-SNE clustering as in (A) but colored by genotype. (C) Left panel: cell-type composition and percentage as colored in (A). Right panel: percentage of cell clusters of the oligodendrocyte lineage. (D) FeaturePlot of a representative gene (Mal) specifically suppressed in MOLs of Stag2f/y;NesCre forebrains. A maximum cutoff of 3 was used. (E) Experimental scheme of the magnetic-activated cell sorting (MACS) of primary OLs. (F) Volcano plot of bulk RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) results of Stag2f/y and Stag2f/y;NesCre primary OLs. (G) The top 5 canonical pathways identified by ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA) of the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) with more than twofold change in (F). The complete gene list is used as the background. (H) Commons DEGs shared between bulk RNA-seq analyses of the whole brains (WB) and primary OLs.