FIGURE 1.
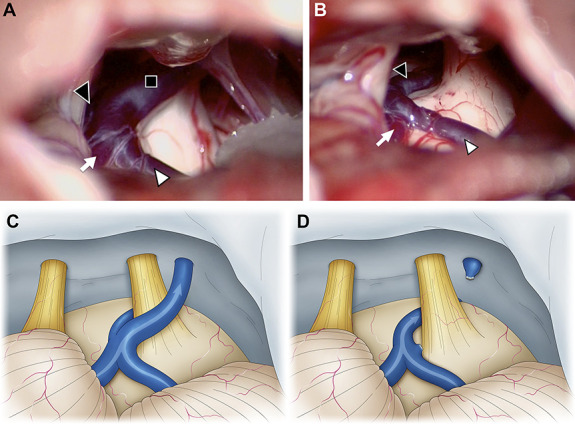
Intraoperative photographs of the second surgery of a 47-year-old woman who underwent microvascular decompression for left trigeminal neuralgia. At the initial surgery, the SCA seemed to be the offending vessel. We performed only transposition of the SCA, but the patient did not experience any postoperative pain relief. Therefore, we concluded that the responsible vessels were the SPV and performed the second surgery. A and C, The SPV (black square) contacts the trigeminal nerve, and its tributaries are the TPV (black arrowhead), the vein of the middle cerebral peduncle (white arrow), and the vein of the cerebellopontine fissure (white arrowhead). B and D, We determined that blood flow from the vein of the middle cerebral peduncle and vein of the cerebral pontine fissure could be drained into the TPV. The SPV was sacrificed, and the blood flow from the vein of cerebellopontine fissure and the vein of middle cerebral peduncle was diverted to the TPV. SCA, superior cerebellar artery; SPV, superior petrosal vein; TPV, transverse pontine vein.
