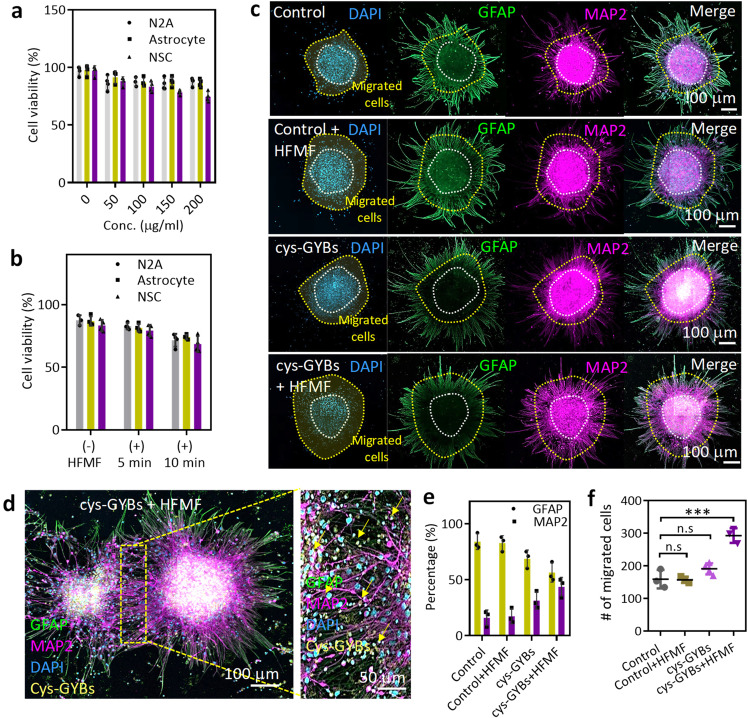
Fig. 4. Electromagnetized cys-GYBs stimulate neuron differentiation.
a Cell viability of NSCs, N2A cells and astrocytes treated with different concentrations of cys-GYBs. Error bars represent mean ± s.d., n = 5. b Cell viability of NSCs, N2A cells and astrocytes treated with 100 μg/ml cys-GYBs with or without HFMF exposure. Error bars represent mean ± s.d., n = 5. c Fluorescence photomicrographs showing the phenotypes of the cells that differentiated from embryonic cerebral cortical neurospheres after 7 days in culture. Anti-MAP-2 (purple) and anti-GFAP (green) antibodies show the immunoreaction of differentiated neurons and astrocytes, respectively. d Magnified images of the GYB + HFMF group. e Quantification of the percentage of differentiation into neurons and astrocytes from neurospheres. Error bars represent mean ± s.d., n = 5. f Quantification of the number of migrated cells in the migrated zone. The cells were cultured under serum-free conditions at 250 neurospheres per cm2 for 7 days. Data represent the mean ± SD (n = 4 per group). ***p < 0.005 compared with the PBS group by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test. Scar bars: 100 mm.