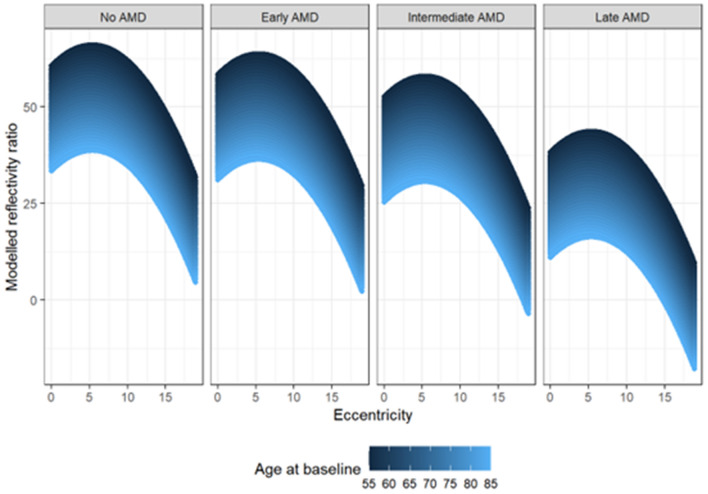
Figure 1.
Graphical representation of linear mixed-effects model analysis with the rEZR as dependent variable and the age at baseline (color-coded in blue: younger age to older age = dark blue to light blue), as well as the topographic variation (eccentricity [°]) of the rEZR from the fovea within each SD-OCT raster scan differentiated for each study group (controls, early AMD, intermediate AMD and late-stage AMD). Note, linear mixed-effects model showed a decreased rEZR in AMD subjects compared to healthy individuals with overall lowest rEZR in the late AMD group followed by the intermediate AMD group. Further, the rEZR was found to first increase and then decrease with increasing eccentricity respecting highest rEZR values at approximately 5° perifoveally within each subgroup. In addition, the rEZR showed an association with subjects’ age at baseline indicated by lower modelled rEZR values in older AMD subjects and controls. AMD age-related macular degeneration.