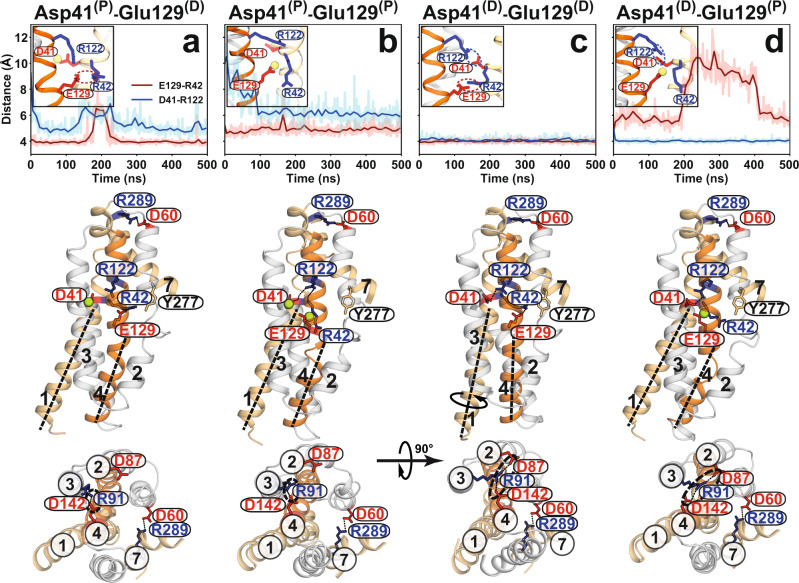
Fig. 6. Proton dependence of luminal salt bridges in HnSpns involving substrate binding residue Arg42.
Time series (light color) and moving averages (dark color) of Glu129-Arg42 (red) and Asp41-Arg122 (blue) side-chain distances from MD simulations of the IF HnSpns structure in the membrane are used to monitor the stability of functionally relevant salt bridges in simulations under different titration states (a–d) of Asp41 and Glu129 (indicated by D and P for deprotonated and protonated, respectively). Data for all simulation replicas are shown in Supplementary Fig. 6. Representative snapshots of the molecular structure from each simulation condition are shown from the side (middle panels) and cytoplasmic (bottom panels) views. Only when Asp41 is deprotonated and interacts with Arg122 can Arg42 completely disengage from protonated Glu129 and bind the substrate (panel d). The Asp41 and Glu129 protonation-dependent conformational changes in TMs 1 and 4 could occur independently of the periplasmic salt bridge stabilizing the extracellular-closed conformation (middle panels). Upon protonation of Asp41, the charge-relay network between Asp87-Arg91-Asp142, which is essential for the conformational transition, cannot be formed, thereby stabilizing the IF conformation (a and b, lower panels).