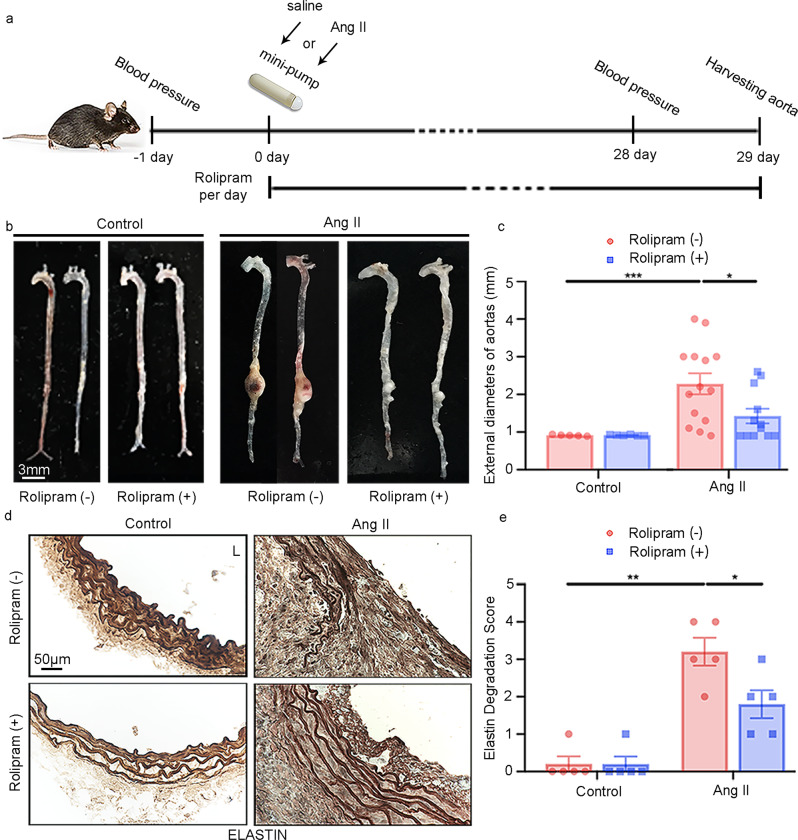
Fig. 4. Effect of rolipram on Ang II-induced AAA in mice.
AAAs were induced by Ang II infusion (1000 ng kg−1 min−1) and an HFD for 28 days, and controls were infused with saline. Rolipram (3 mg kg−1 d−1) was orally administered daily for 28 days. Mouse AAA aortas were dissected at the maximal suprarenal outer aortic diameter, and controls were collected from corresponding suprarenal abdominal aortas of the control mice. a Schematic diagram of the mouse model of Ang II-induced AAA treated with vehicle or rolipram. Vehicle (n = 5) and rolipram (n = 6) with saline infusion, vehicle (n = 14) and rolipram (n = 12) with Ang II infusion. b Representative images of entire aortas of the Apoe−/− mice treated with vehicle or rolipram. c Quantification of the maximal external diameter (mm) of the abdominal aorta measured by two different investigators using a stereoscope. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, Welch’s t test between the rolipram (−) control and rolipram (−) Ang II groups, Mann–Whitney test between the rolipram (−) Ang II and rolipram (+) Ang II groups, mean ± SEM, vehicle (n = 5) and rolipram (n = 6) with saline infusion, vehicle (n = 14) and rolipram (n = 12) with Ang II infusion. d Representative images of elastin staining of the mouse arterial wall. L: lumen. e Quantification of the elastin degradation score from the four indicated groups in (d). Elastin staining is indicated by the darkest color. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, Mann–Whitney test between the rolipram (−) control and rolipram (−) Ang II groups, unpaired Student’s t test between the rolipram (−) Ang II and rolipram (+) Ang II groups, mean ± SEM, vehicle (n = 5) and rolipram (n = 5) with saline infusion, vehicle (n = 5) and rolipram (n = 5) with Ang II infusion.