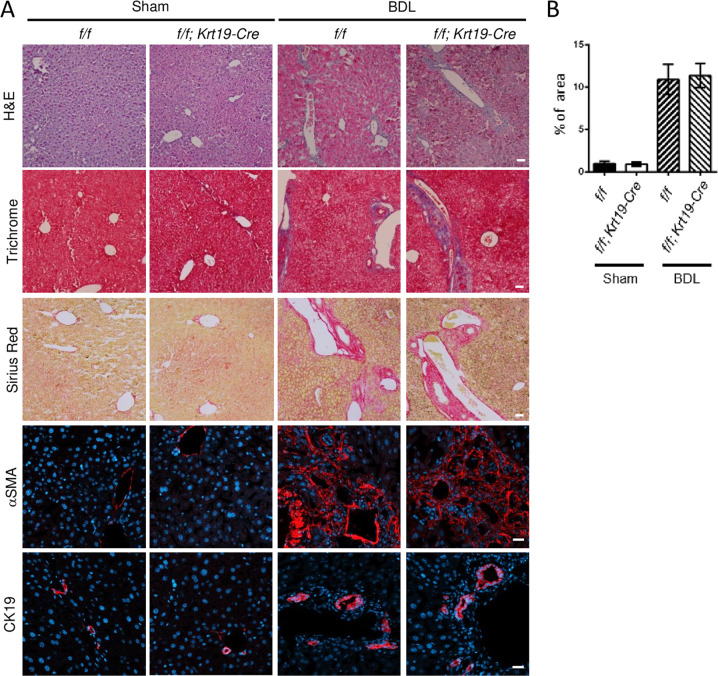
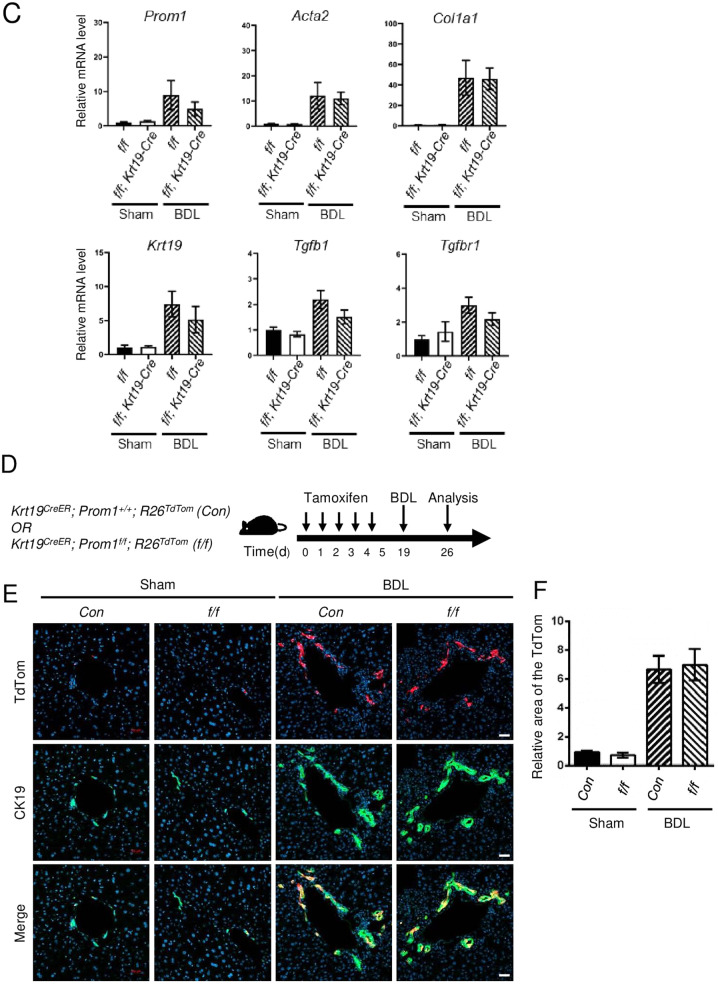
Fig. 3. Cholangiocyte-specific Prom1 deficiency did not affect BDL-induced liver fibrosis.
A–C Eight-week-old male Prom1f/f (f/f) and Prom1f/f; Krt19-Cre (f/f; Krt19-Cre) mice were subjected to sham surgery (n = 3) or BDL (n = 7–9) for one week. A Each liver specimen was subjected to H&E, Masson’s trichrome and Sirius Red staining, and immunofluorescence analysis of αSMA and CK19. B Liver fibrosis was quantified by measuring the areas stained with Sirius Red. Two to three images of each liver showing Sirius Red staining were obtained. C The mRNA levels of Prom1, Acta2, Col1a1, Krt19, Tgfbr1, and Tgfb1 were determined by RT–qPCR and normalized to those of 18S rRNA. D–F Krt19CreER; Prom1+/+; R26TdTom (Con) and Krt19CreER; Prom1f/f; R26TdTom (f/f) mice were generated for the lineage tracing of CK19-expressing cells. Six-week-old male mice were injected with tamoxifen. Two weeks after injection, the mice were subjected to sham surgery (n = 3) and BDL (n = 7) for 1 week (D). Each liver specimen was analyzed by TdTom fluorescence analysis and CK19 immunofluorescence analysis (E). Statistical analysis of TdTom-expressing cells in E. The TdTom fluorescence area was normalized to DAPI-stained dots (F). Scale bar = 20 µm. All data are the mean ± S.E.M. Con, control.