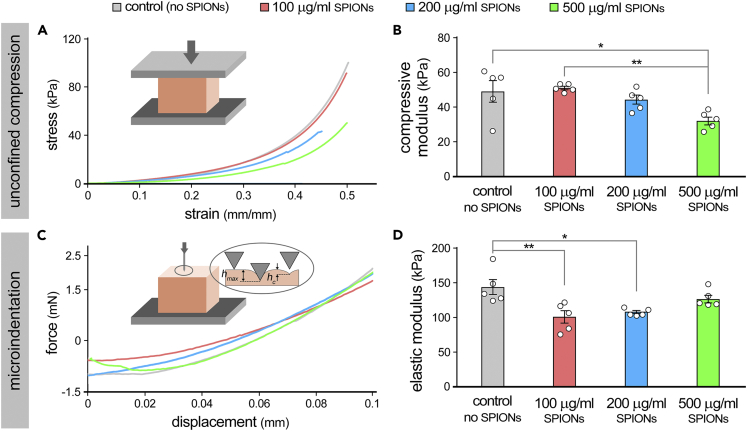
Figure 3.
Mechanical characterization of bioprinted constructs loaded with varying quantities of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs)
(A and B) Unconfined compression test conducted (at a 50% total strain at 20 μm/s) on bioprinted GelMA scaffolds containing no SPIONs (control), 100, 200, and 500 μg/mL SPIONs (n = 4 per group). Elastic moduli (B) were calculated from the slope of the stress-strain curves at the initial 0%–20% interval.
(C and D) Microindentation tests were conducted on GelMA constructs using a 500 μm probe, with a depth of 100 μm at 2 μm/s (n = 5 per group). Elastic moduli were calculated based on the force-displacement unloading curves as described in STAR Methods (the slope of the linear trend line at initial 5–20%). ∗ p value < 0.05, ∗∗ p value < 0.01.